Simulation-Based Inference for Cosmology
SLAC Summer Institute, August 2023
François Lanusse



slides at eiffl.github.io/talks/SSI2023/sbi.html
Let's set the stage: Gravitational lensing
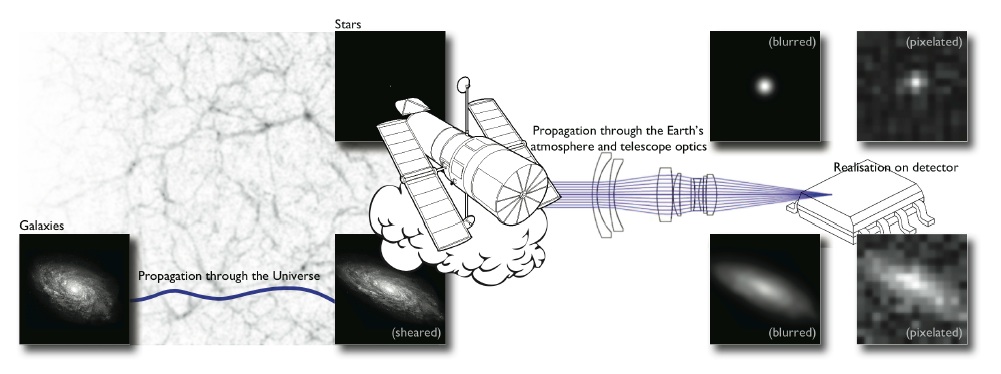
Galaxy shapes as estimators for gravitational shear
$$ e = \gamma + e_i \qquad \mbox{ with } \qquad e_i \sim \mathcal{N}(0, I)$$
- We are trying the measure the ellipticity $e$ of galaxies as an estimator for the gravitational shear $\gamma$
The limits of traditional cosmological inference
HSC cosmic shear power spectrum
HSC Y1 constraints on $(S_8, \Omega_m)$
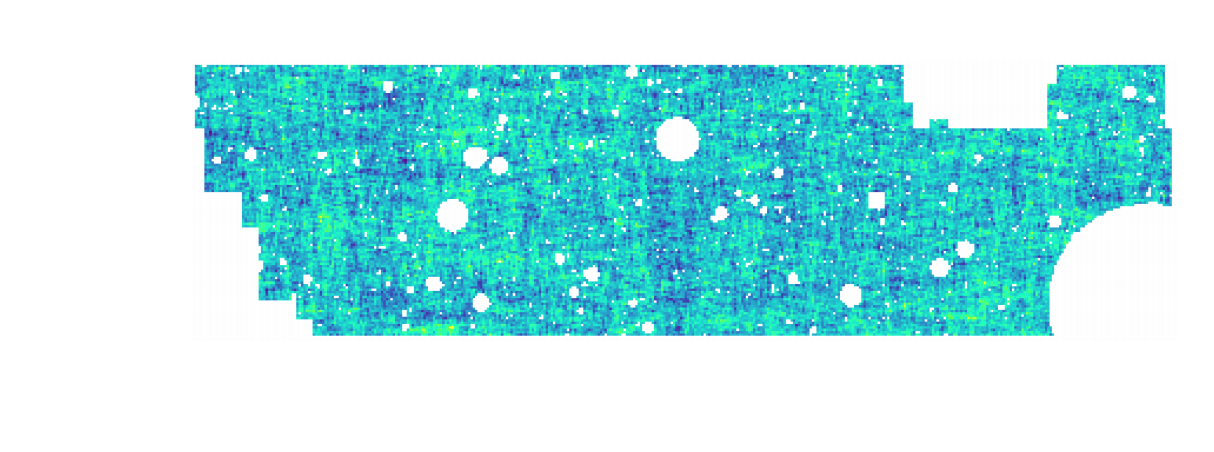
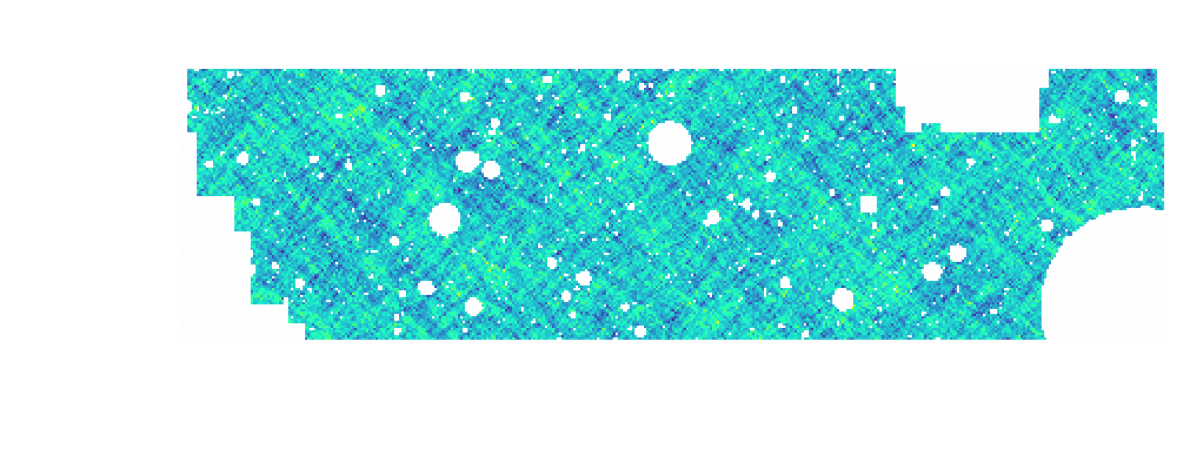
(Hikage et al. 2018)
- Measure the ellipticity $\epsilon = \epsilon_i + \gamma$ of all galaxies
$\Longrightarrow$ Noisy tracer of the weak lensing shear $\gamma$ - Compute summary statistics based on 2pt functions,
e.g. the power spectrum - Run an MCMC to recover a posterior on model parameters, using an analytic likelihood $$ p(\theta | x ) \propto \underbrace{p(x | \theta)}_{\mathrm{likelihood}} \ \underbrace{p(\theta)}_{\mathrm{prior}}$$
Main limitation: the need for an explicit likelihood
We can only compute from theory the likelihood for simple summary statistics and on large scales
$\Longrightarrow$ We are dismissing a significant fraction of the information!
Full-Field Simulation-Based Inference
- Instead of trying to analytically evaluate the likelihood of
sub-optimal summary statistics, let us build a forward model of the full observables.
$\Longrightarrow$ The simulator becomes the physical model. - Each component of the model is now tractable, but at the cost of a large number of latent variables.
Benefits of a forward modeling approach
- Fully exploits the information content of the data (aka "full field inference").
- Easy to incorporate systematic effects.
- Easy to combine multiple cosmological probes by joint simulations.
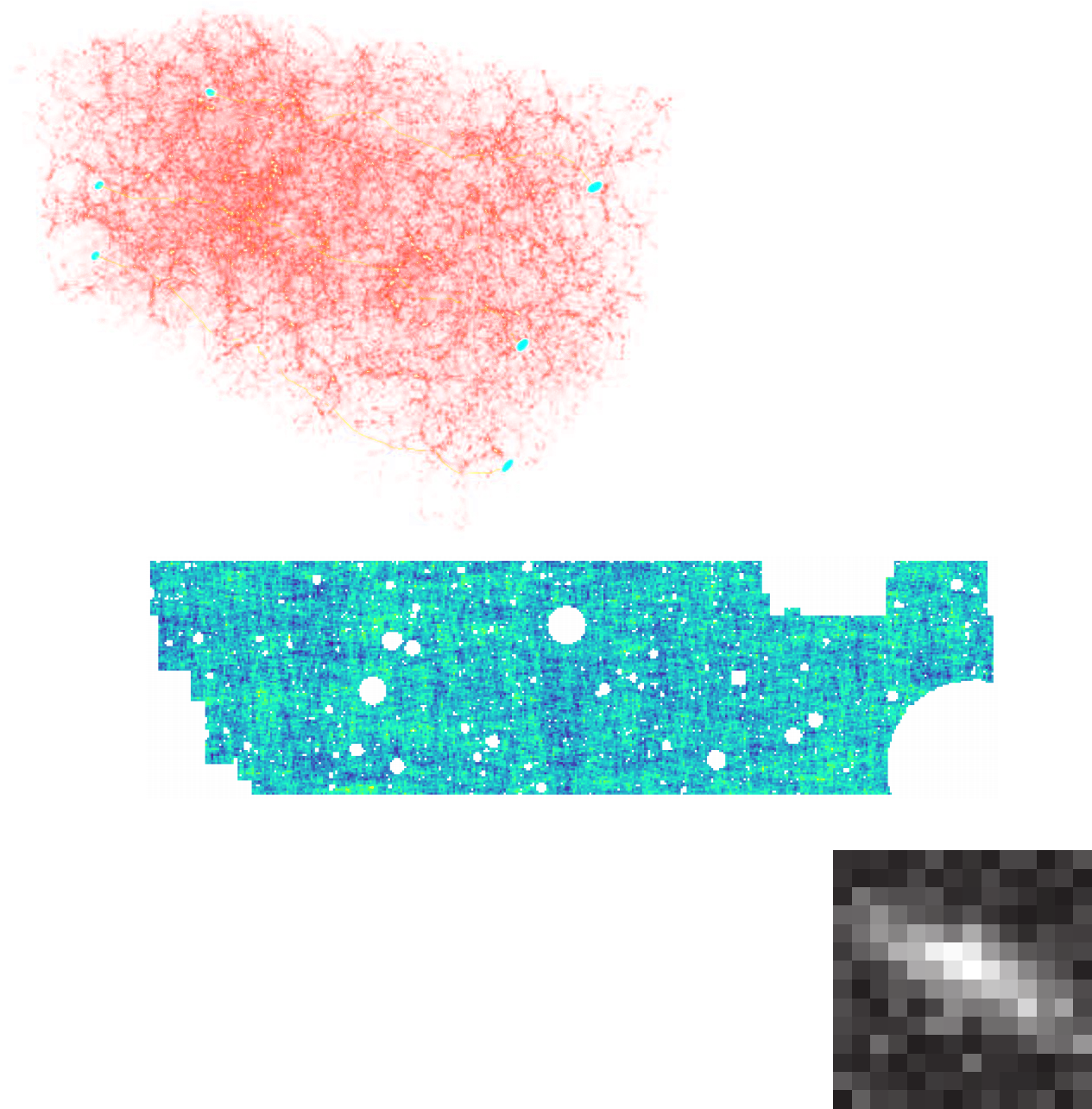
(Porqueres et al. 2021)
For now, let's ignore the elephant in the room:
Do we have reliable enough models for the full complexity of the data?
Do we have reliable enough models for the full complexity of the data?
...so why is this not mainstream?
The Challenge of Simulation-Based Inference
$$ p(x|\theta) = \int p(x, z | \theta) dz = \int p(x | z, \theta) p(z | \theta) dz $$
Where $z$ are stochastic latent variables of the simulator.
$\Longrightarrow$ This marginal likelihood is intractable!
$\Longrightarrow$ This marginal likelihood is intractable!
How to perform inference over forward simulation models?
- Implicit Inference: Treat the simulator as a black-box with only the ability to sample from the joint distribution
$$(x, \theta) \sim p(x, \theta)$$
a.k.a.
- Simulation-Based Inference (SBI)
- Likelihood-free inference (LFI)
- Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC)
- Explicit Inference: Treat the simulator as a probabilistic model and perform inference over the joint posterior
$$p(\theta, z | x) \propto p(x | z, \theta) p(z, \theta) p(\theta) $$
a.k.a.
- Bayesian Hierarchical Modeling (BHM)
$\Longrightarrow$ For a given simulation model, both methods should converge to the same posterior!
Implicit Inference
The land of Neural Density Estimation
Black-box Simulators Define Implicit Distributions

- A black-box simulator defines $p(x | \theta)$ as an implicit distribution, you can sample from it but you cannot evaluate it.
- This gives us a procedure to sample from the Bayesian joint distribution $p(x, \theta)$: $$(x, \theta) \sim p(x | \theta) \ p(\theta)$$
- Key Idea: Use a parametric distribution model $\mathbb{P}_\varphi$ to approximate an implicit distribution.
- Neural Likelihood Estimation: $\mathcal{L} = - \mathbb{E}_{(x,\theta)}\left[ \log p_\varphi( x | \theta ) \right] $
- Neural Posterior Estimation: $\mathcal{L} = - \mathbb{E}_{(x,\theta)}\left[ \log p_\varphi( \theta | x ) \right] $
- Neural Ratio Estimation: $\mathcal{L} = - \mathbb{E}_{\begin{matrix} (x,\theta)~p(x,\theta) \\ \ \theta^\prime \sim p(\theta) \end{matrix}} \left[ \log r_\varphi(x,\theta) + \log(1 - r_\varphi(x, \theta^\prime)) \right] $
A variety of algorithms
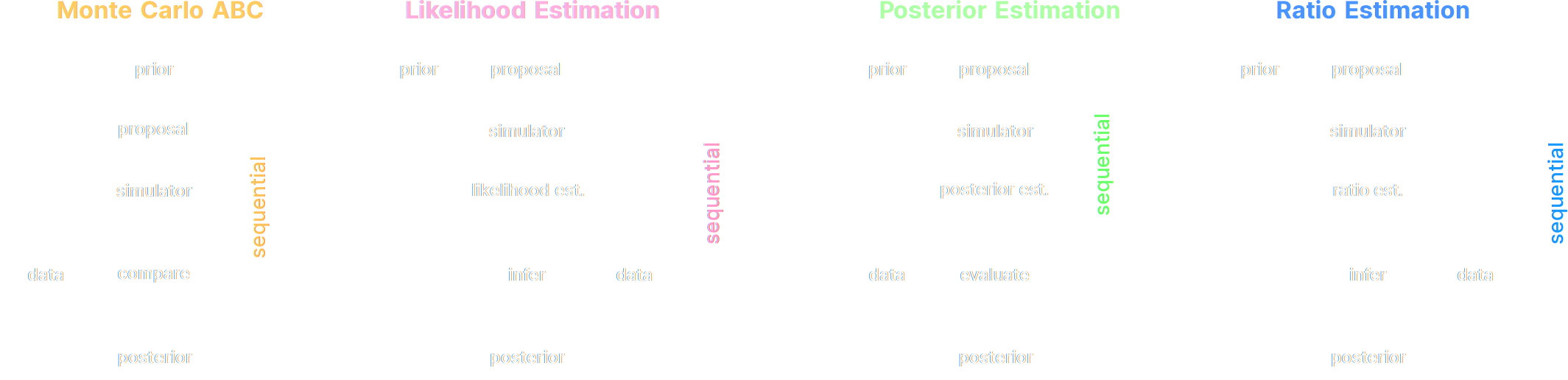
A few important points:
- Amortized inference methods, which estimate $p(\theta | x)$, can greatly speed up posterior estimation once trained.
- Sequential SBI algorithms can actively sample simulations needed to refine the inference.
Checkout this excellent package: https://www.mackelab.org/sbi
A Practical Recipe for Careful Simulation-Based Inference
Estimating conditional densities
in high dimensions is hard...
To be more robust, you can decompose the problem into two tasks:
- Step I - Dimensionality Reduction: Compress your observables $x$ to a low dimensional summary statistic $y$
![]()
- Step II - Conditional Density Estimation: Estimate the posterior $p(\theta | y)$ using SBI from the low dimensional summary statistic $y$.
The Case for Dimensionality Reduction
- In the case of Neural Posterior Estimation
![]()
![]() $p(\theta | x)$$\Longrightarrow$ Dimensionality reduction already happens implicitly in the network.
$p(\theta | x)$$\Longrightarrow$ Dimensionality reduction already happens implicitly in the network. - In the case of Neural Likelihood Estimation
![]() $x \sim p(x|\theta)$
$x \sim p(x|\theta)$
![]() $\theta$$\Longrightarrow$ This is equivalent to learning a perfect emulator for the high-dimensional outputs of your numerical simulator.
$\theta$$\Longrightarrow$ This is equivalent to learning a perfect emulator for the high-dimensional outputs of your numerical simulator.
How can we lower the dimensionality of the problem without degrading our constraining power?
Automated Neural Summarization
- Introduce a parametric function $f_\varphi$ to reduce the dimensionality of the data while preserving information.
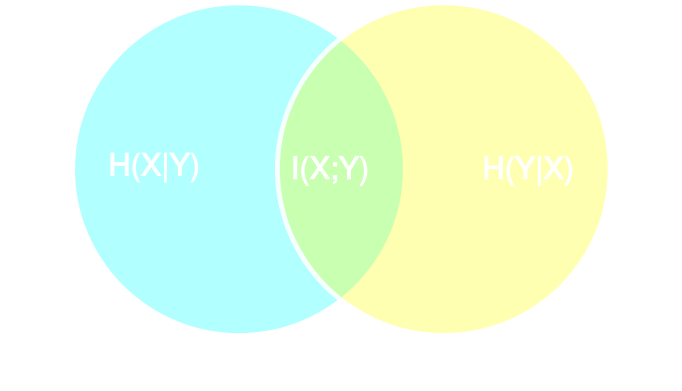
Information point of view
- Summary statistics $y$ is sufficient for $\theta$ if $$ I(Y; \Theta) = I(X; \Theta) \Leftrightarrow p(\theta | x ) = p(\theta | y) $$
- Variational Mutual Information Maximization $$ \mathcal{L} \ = \ \mathbb{E}_{x, \theta} [ \log q_\phi(\theta | y=f_\varphi(x)) ] \leq I(Y; \Theta) $$ (Barber & Agakov variational lower bound)
Another Approach: maximizing the Fisher information
 Information Maximization Neural Network (IMNN)
$$\mathcal{L} \ = \ - | \det \mathbf{F} | \ \mbox{with} \ \mathbf{F}_{\alpha, \beta} = tr[ \mu_{\alpha}^t C^{-1} \mu_{\beta} ] $$
Information Maximization Neural Network (IMNN)
$$\mathcal{L} \ = \ - | \det \mathbf{F} | \ \mbox{with} \ \mathbf{F}_{\alpha, \beta} = tr[ \mu_{\alpha}^t C^{-1} \mu_{\beta} ] $$
Full-Field Implicit Inference
by Neural Summarisation and Density Estimation
Work led by Denise Lanzieri and Justine Zeghal

$\Longrightarrow$ Demonstrating that neural summary statistics exhaust the cosmological information content.
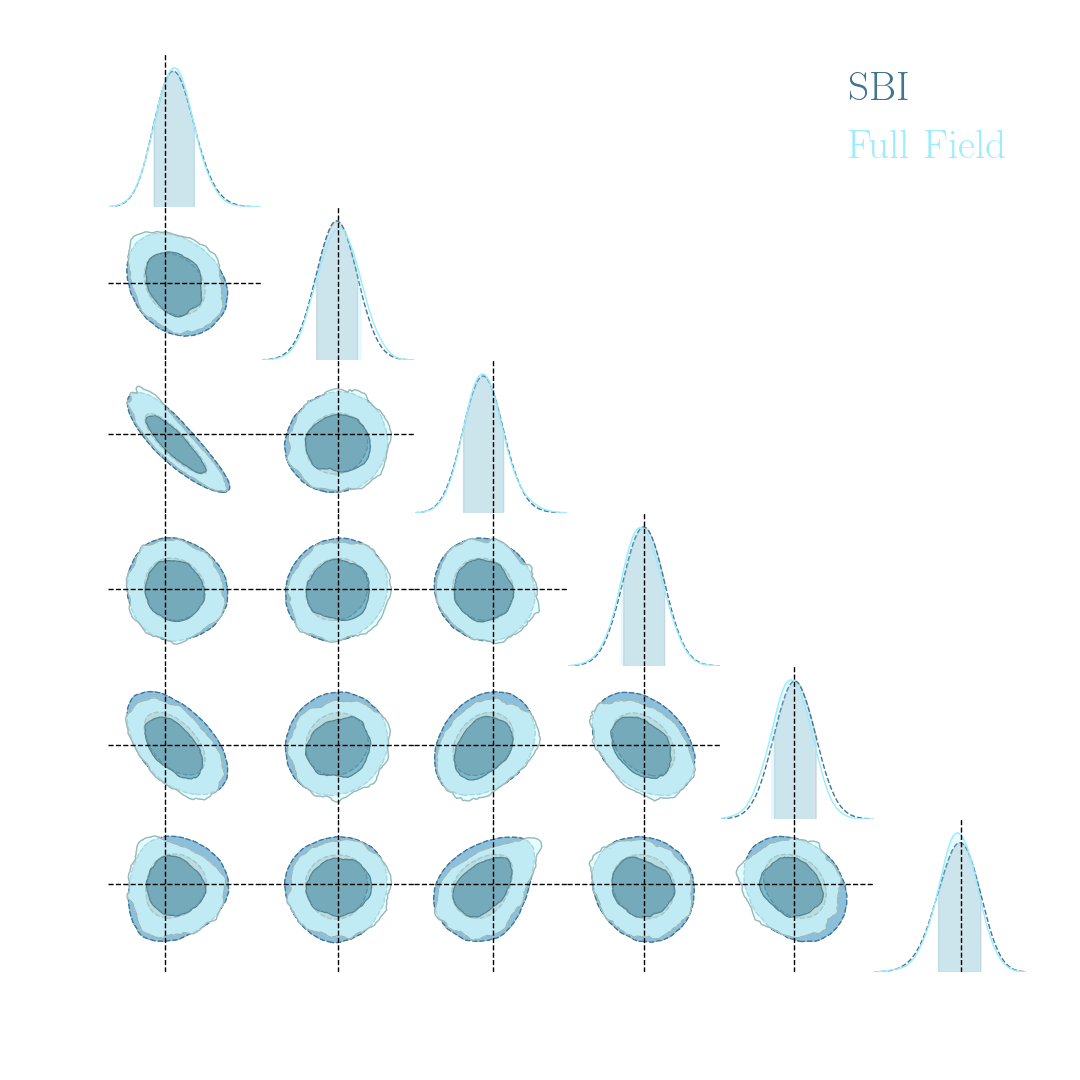
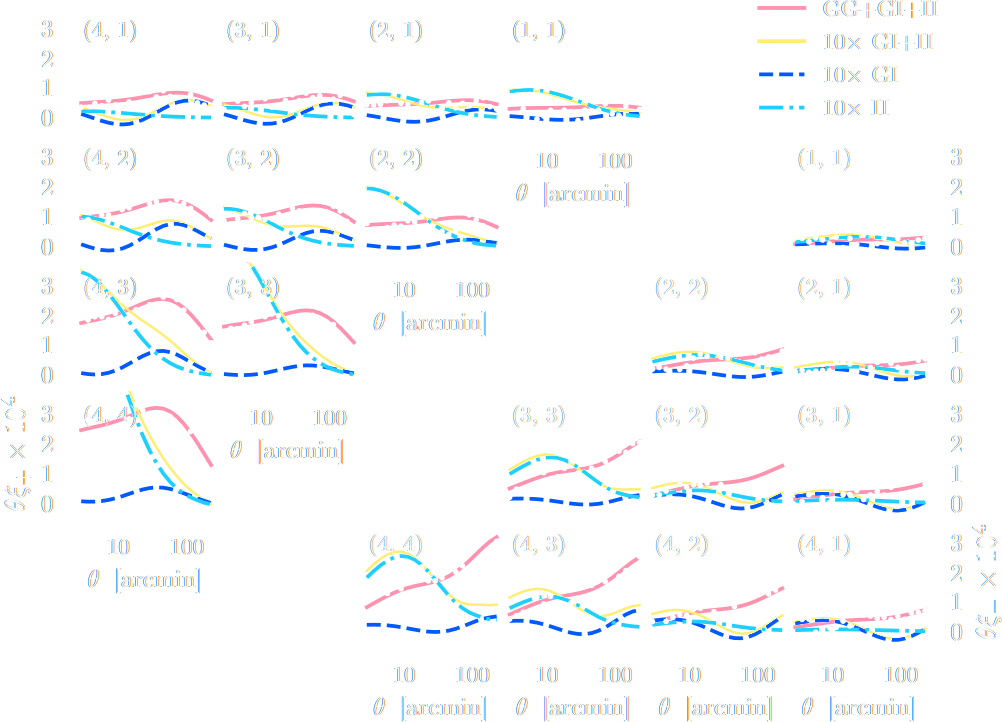
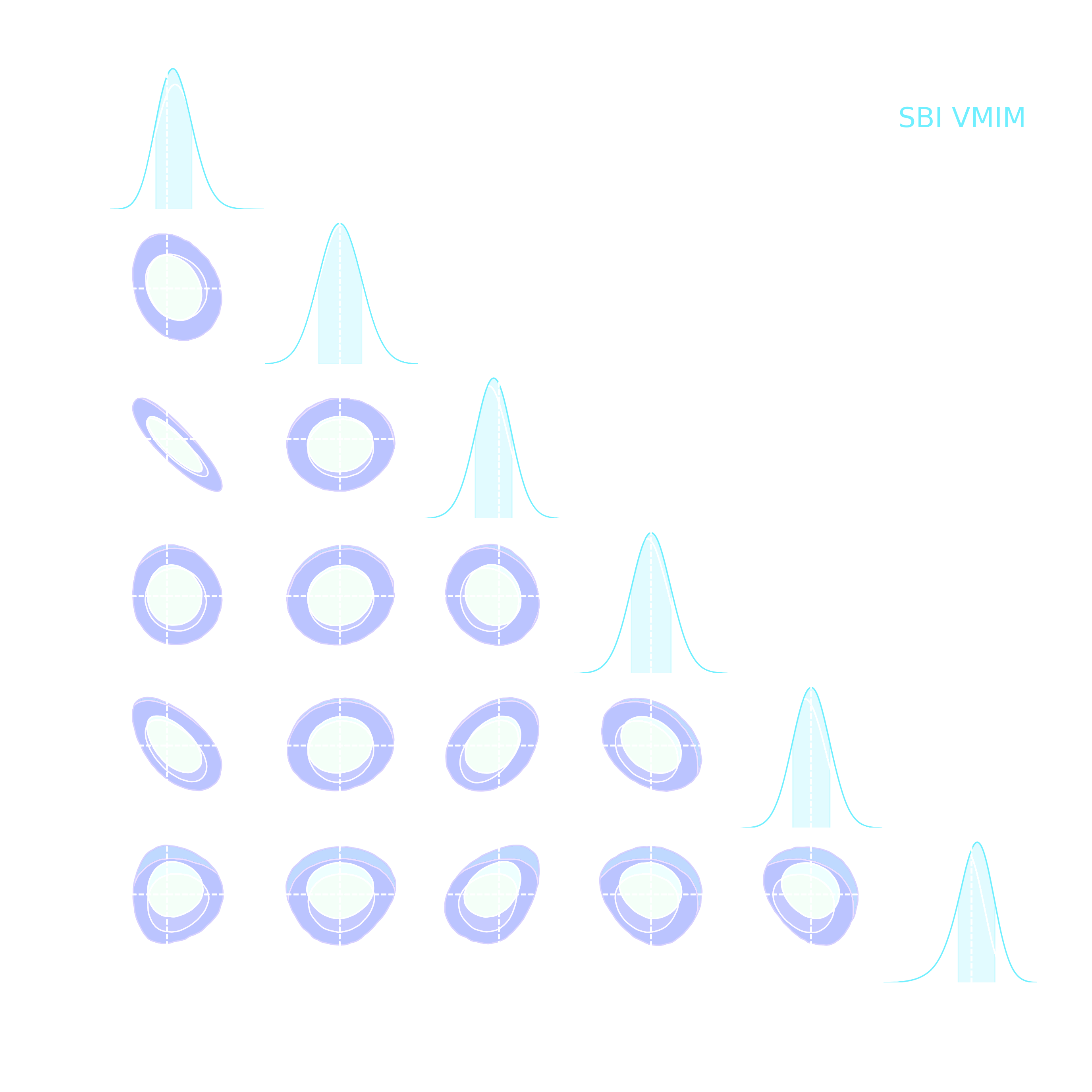
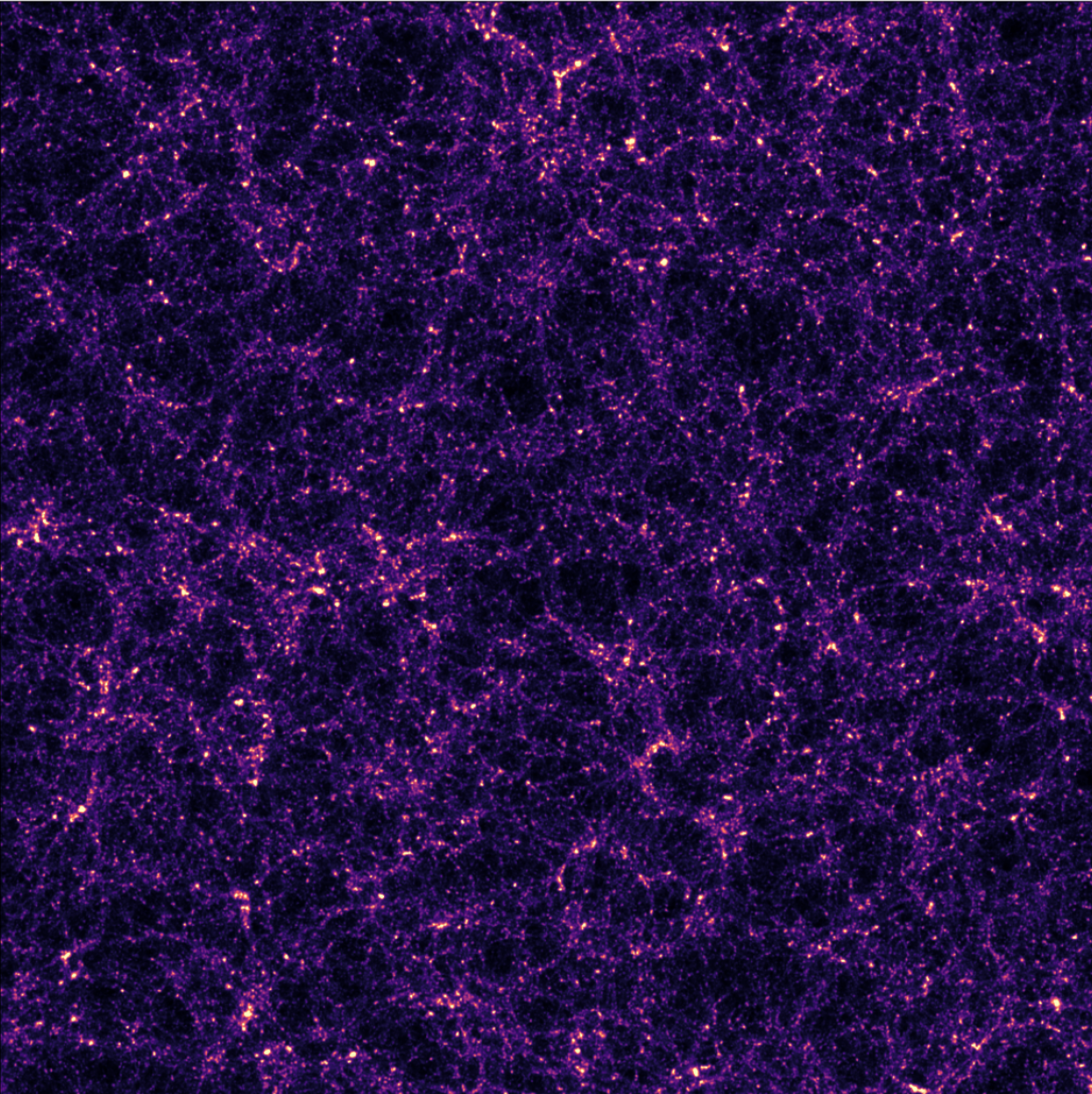
An easy-to-use validation testbed: log-normal lensing simulations

DifferentiableUniverseInitiative/sbi_lens
JAX-based log-normal lensing simulation package

- 10x10 deg$^2$ maps at LSST Y10 quality, conditioning the log-normal shift parameter on $(\Omega_m, \sigma_8, w_0)$
- Infer full-field posterior on cosmology:
- explicitly using an Hamiltonian-Monte Carlo (NUTS) sampler
- implicitly using a learned summary statistics and conditional density estimation.
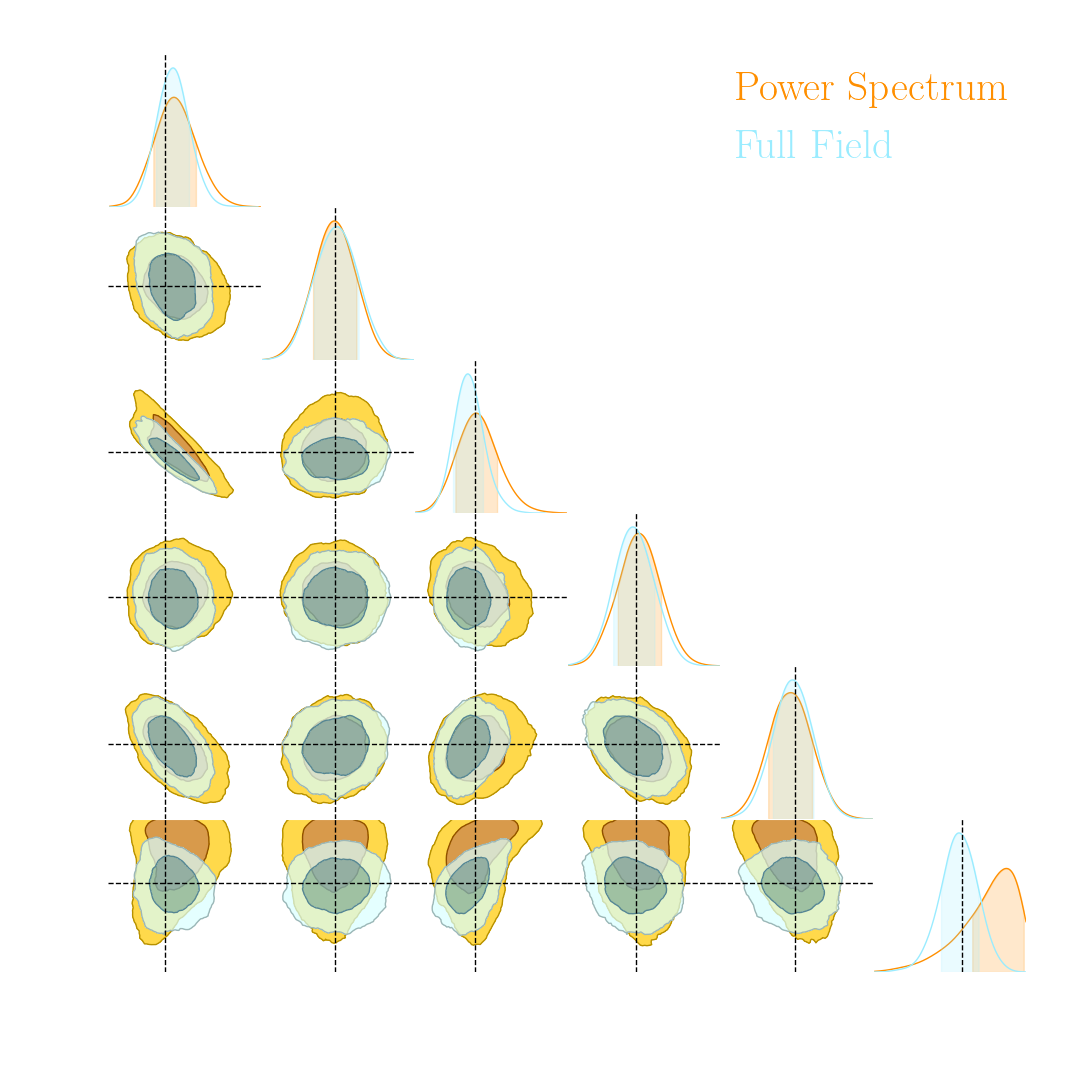


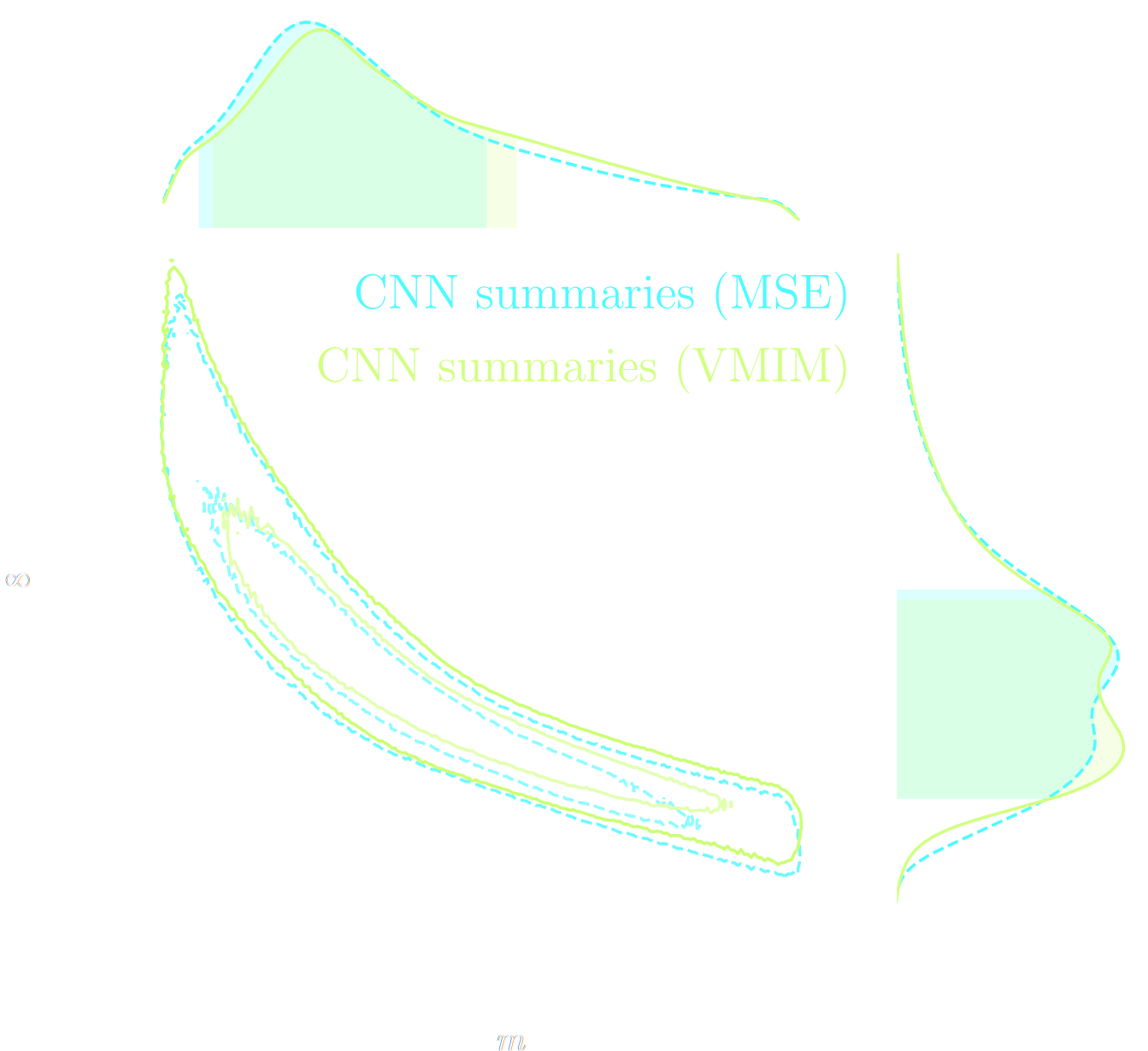
Note: not all compression techniques are equivalent!
- Comparison to posteriors obtained with same neural compression architecture, but different loss function: $$\mathcal{L}_{MSE} = \mathbb{E}_{(x,\theta)} || f_\varphi(x) - \theta ||_2^2 $$

Likelihood-free inference with neural compression of DES SV weak lensing map

Work in collaboration with Niall Jeffrey, Justin Alsing


$\Longrightarrow$ Deploy end-to-end SBI to the Science Verification data of the Dark Energy Survey.
End-to-end framework for likelihood-free parameter inference with DES SV

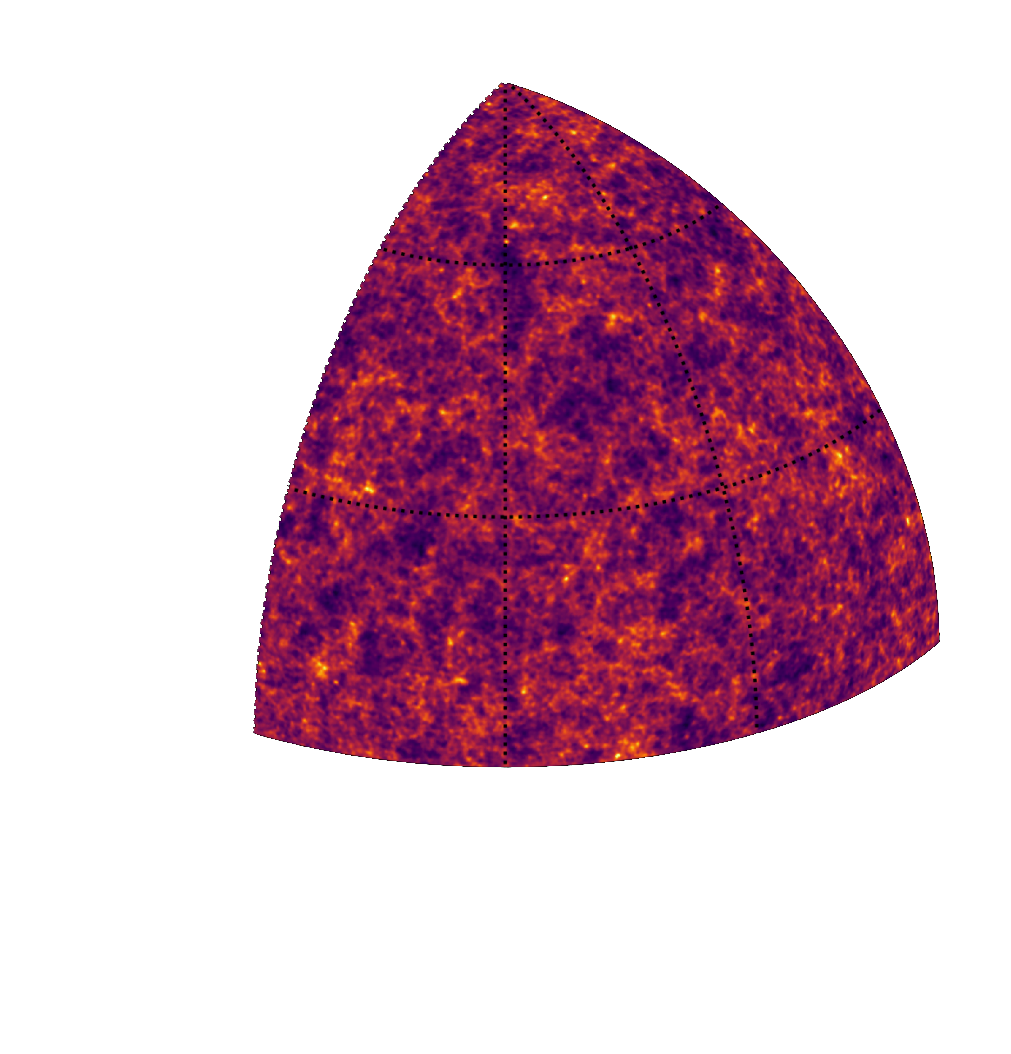
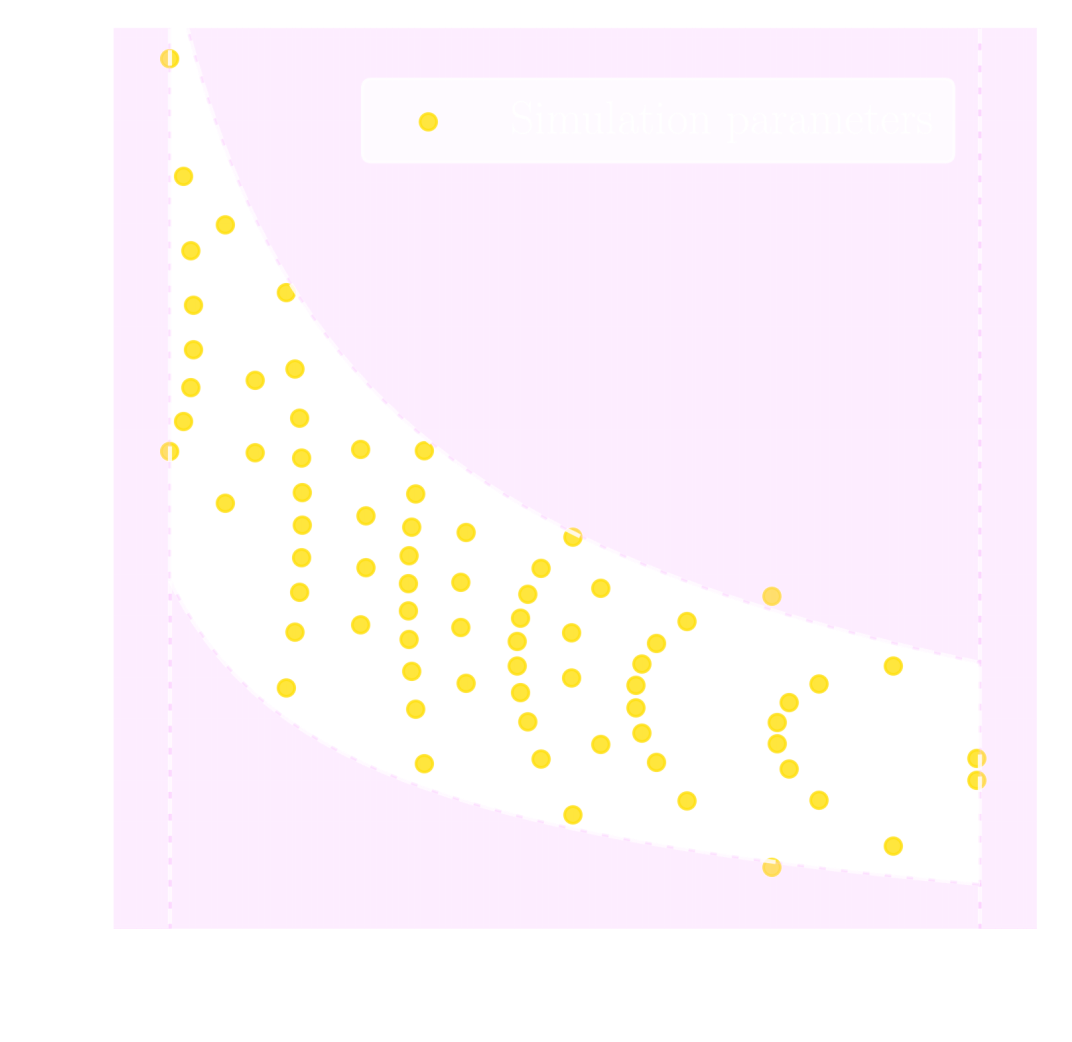
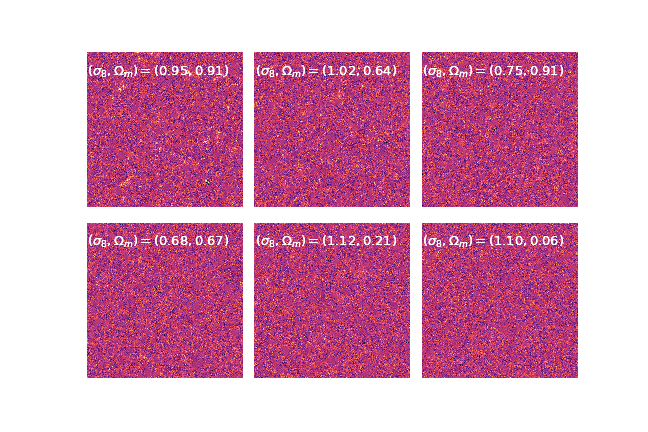
Suite of N-body + raytracing simulations: $\mathcal{D}$
deep residual networks for lensing maps compression
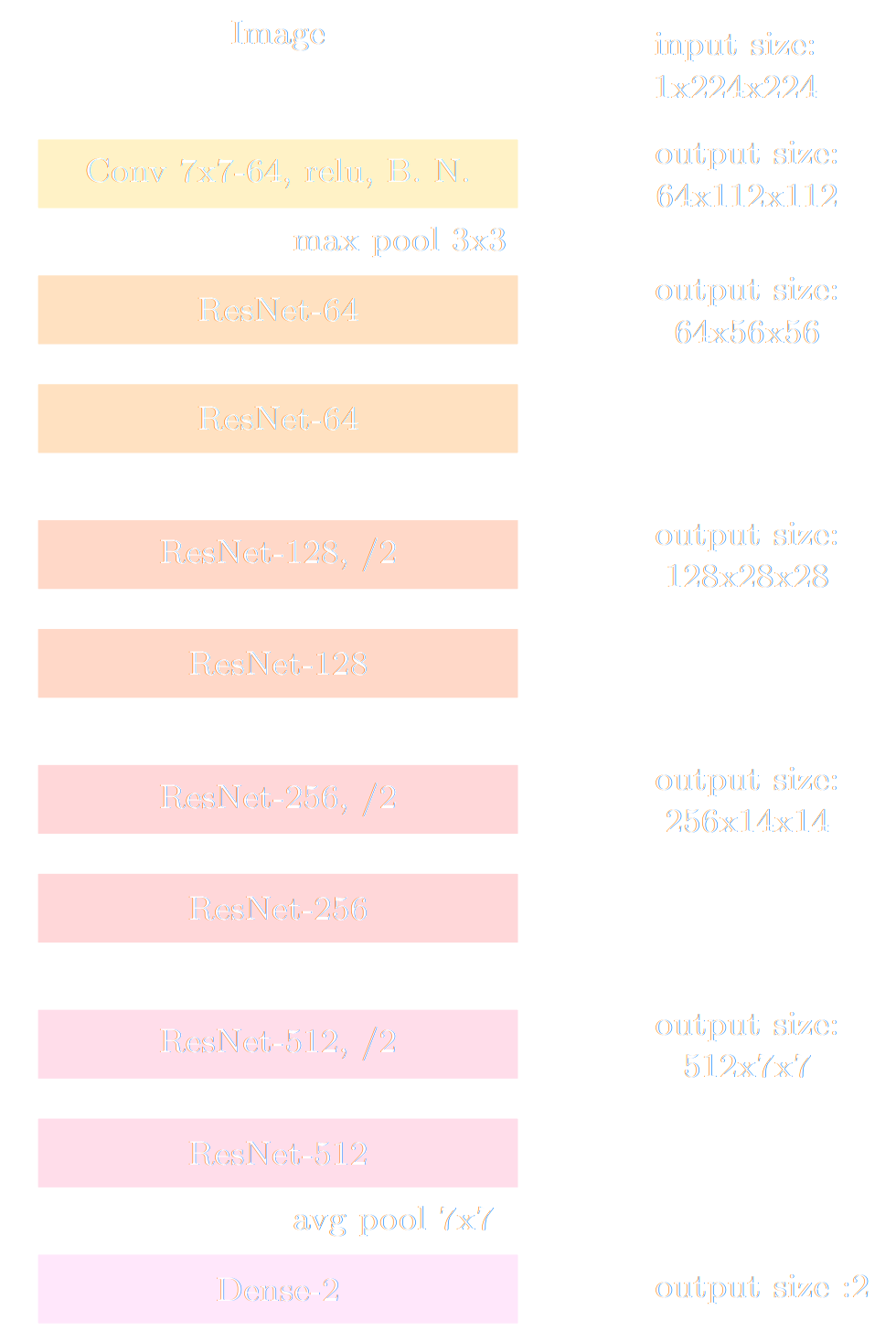
- Deep Residual Network $y = f_\phi(x)$ followed by neural density estimator $q_\phi(\theta | y)$
- Training on weak lensing maps simulated for different cosmologies
- Training by Variational Mutual Information Maximization: $$\mathbb{E}_{(x, \theta) \in \mathcal{D}} [ \log q_\phi(\theta | y = f_\phi(x) ) ]$$


Estimating the likelihood by Neural Density Estimation
$\Longrightarrow$ We cannot assume a Gaussian likelihood for the summary $y = f_\phi(\kappa)$ but we can learn $p(y | \theta)$: Neural Likelihood Estimation.
Dinh et al. 2016
Neural Likelihood Estimation by Normalizing Flow
- We use a conditional Normalizing Flow to build an explicit model for the likelihood function $$ \log p_\varphi (y | \theta)$$
- In practice we use the pyDELFI package and an ensemble of NDEs for robustness.
- Once learned, we can use the likelihood as part of a conventional MCMC chain
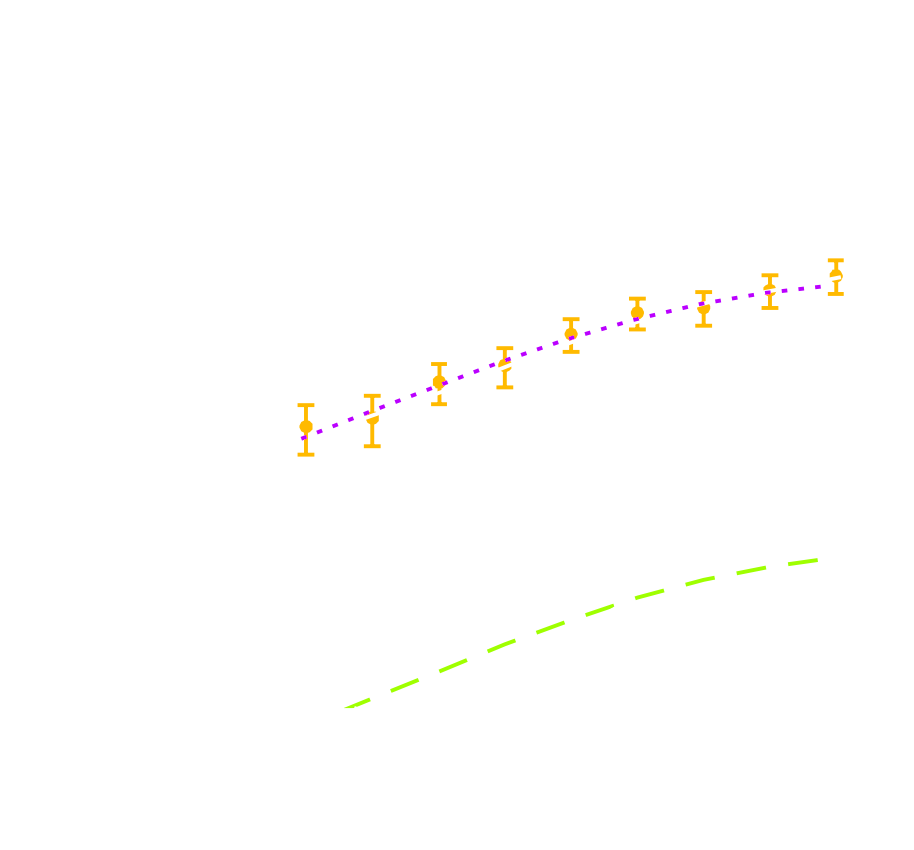
Parameter constraints from DES SV data
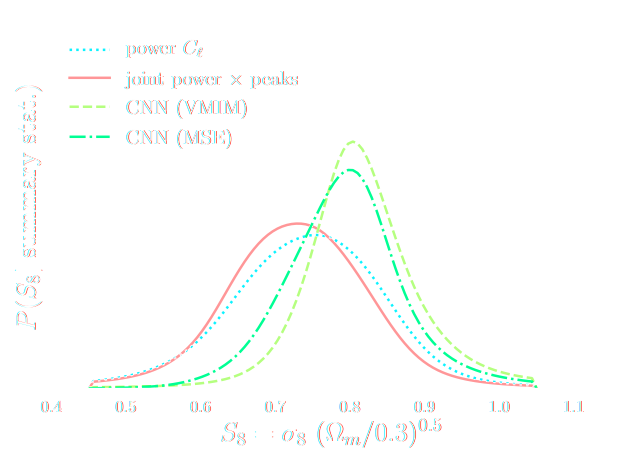
Can we just retire all conventional likelihood-based analyses?
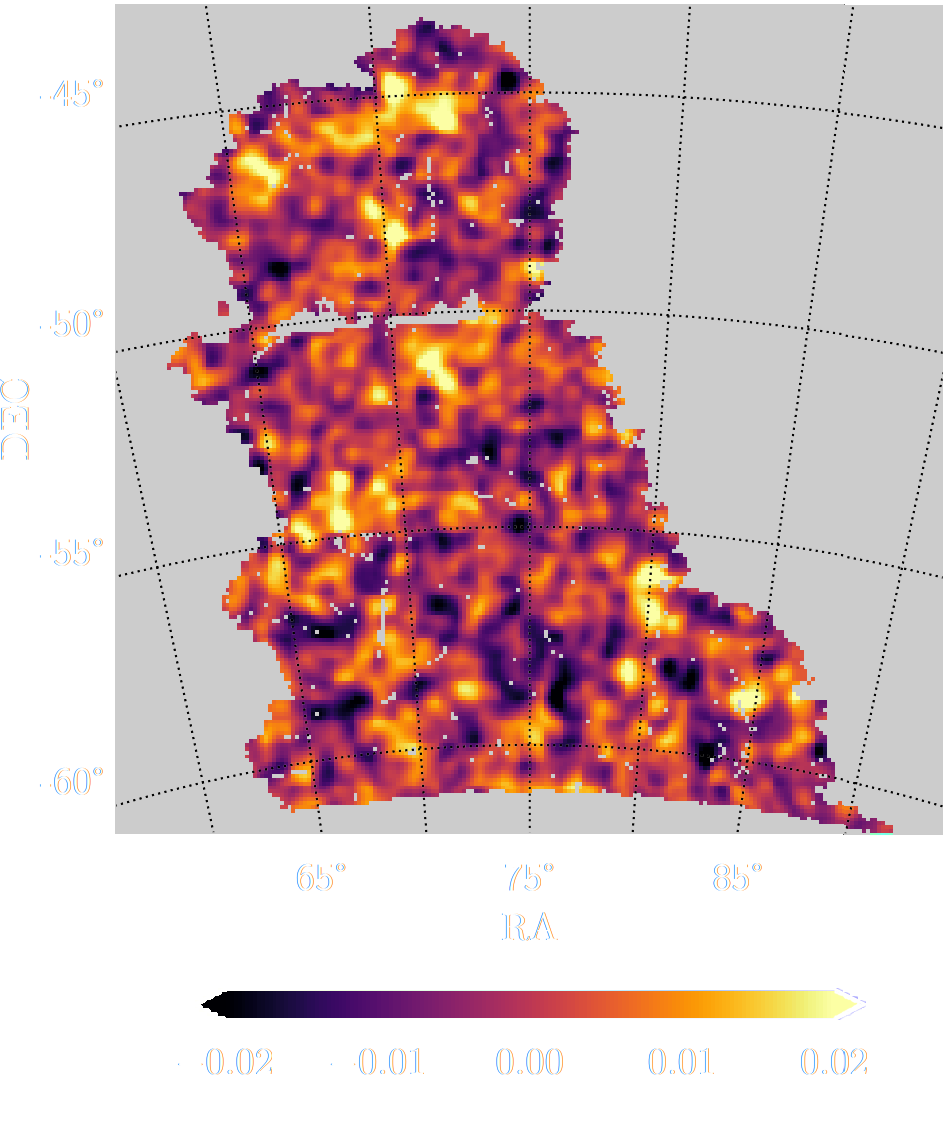
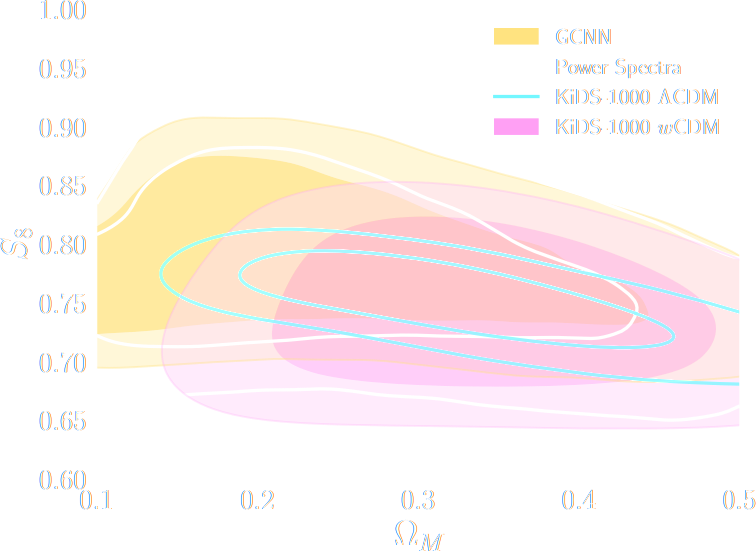
$w$CDM analysis of KiDS-1000 Weak Lensing (Fluri et al. 2022)
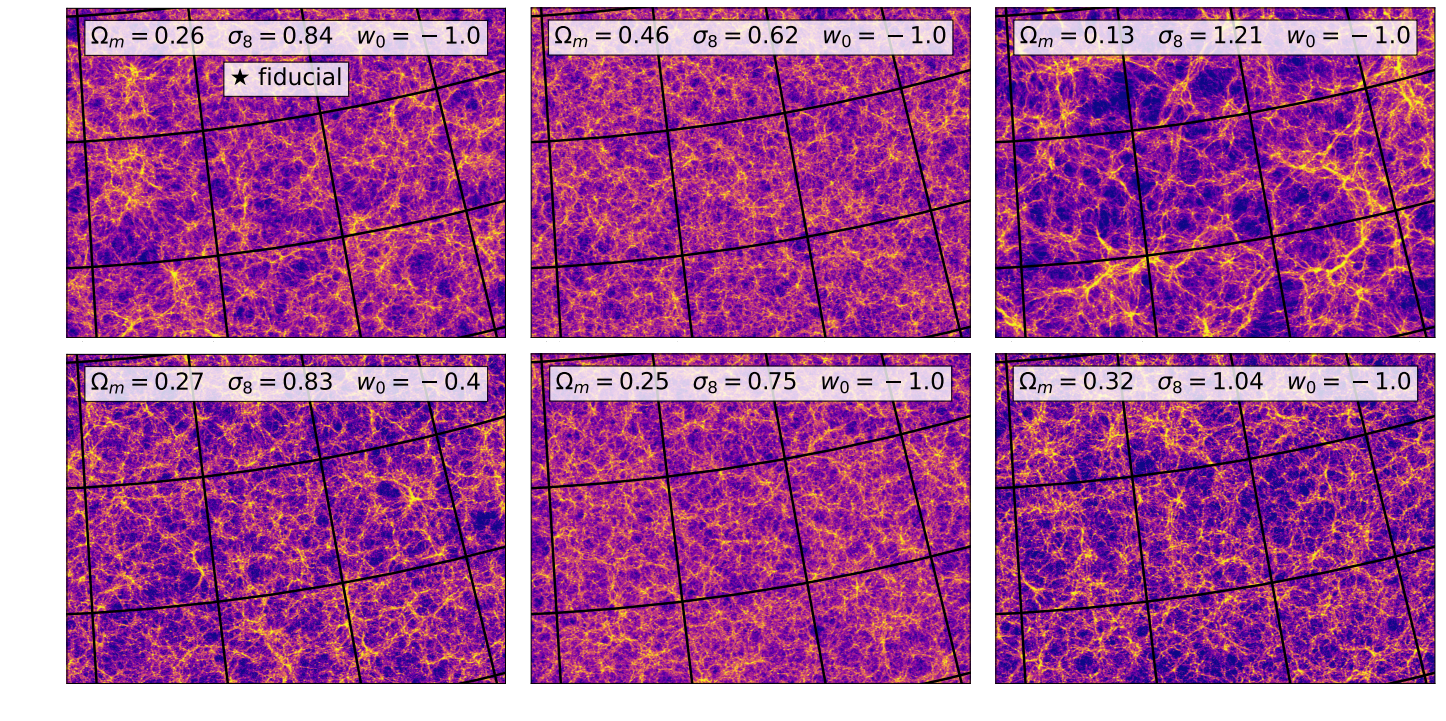
CosmoGridV1 simulations, available at http://www.cosmogrid.ai
- 17,500 simulations at 2,500 cosmologies
- Lensing, Intrinsic Alignment, and Galaxy Density
maps at nside=512
KiDS-1000 footprint and simulated data
![]()
- Neural Compressor: Graph Convolutional Neural Network on the Sphere
Trained by Fisher information maximization.
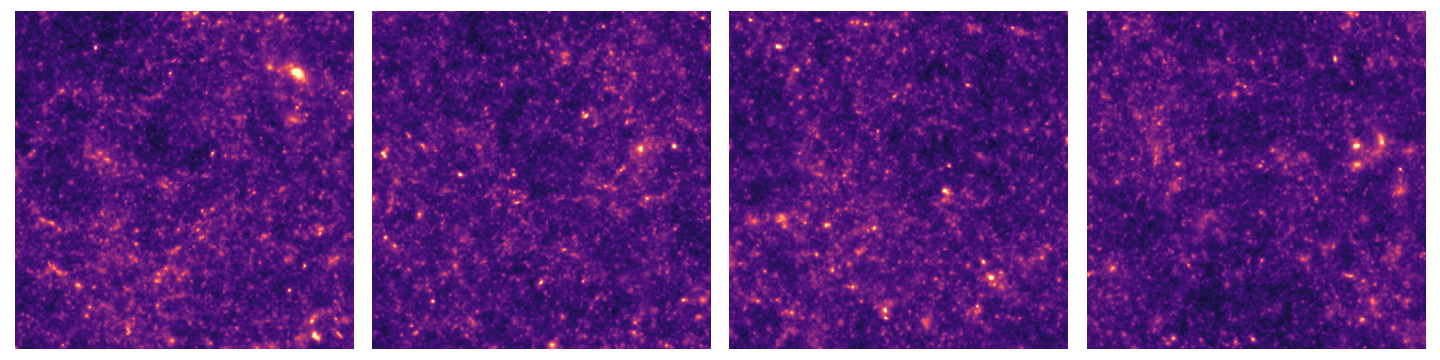
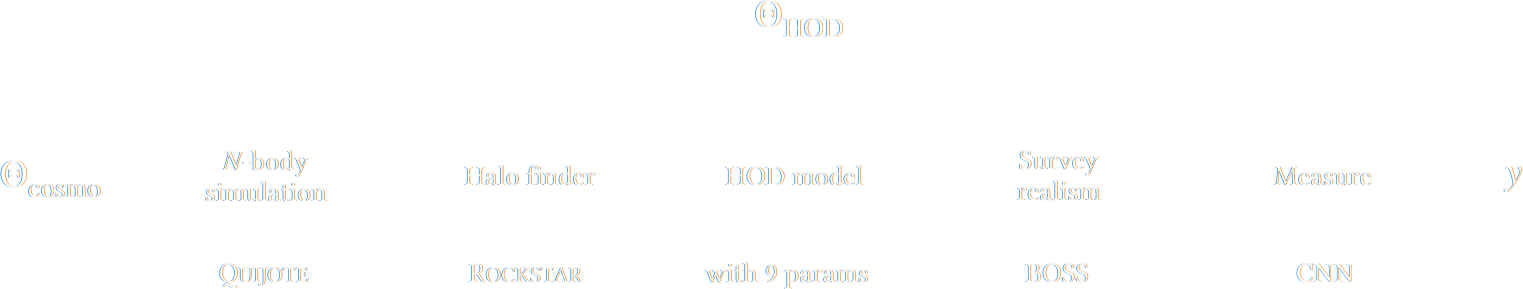
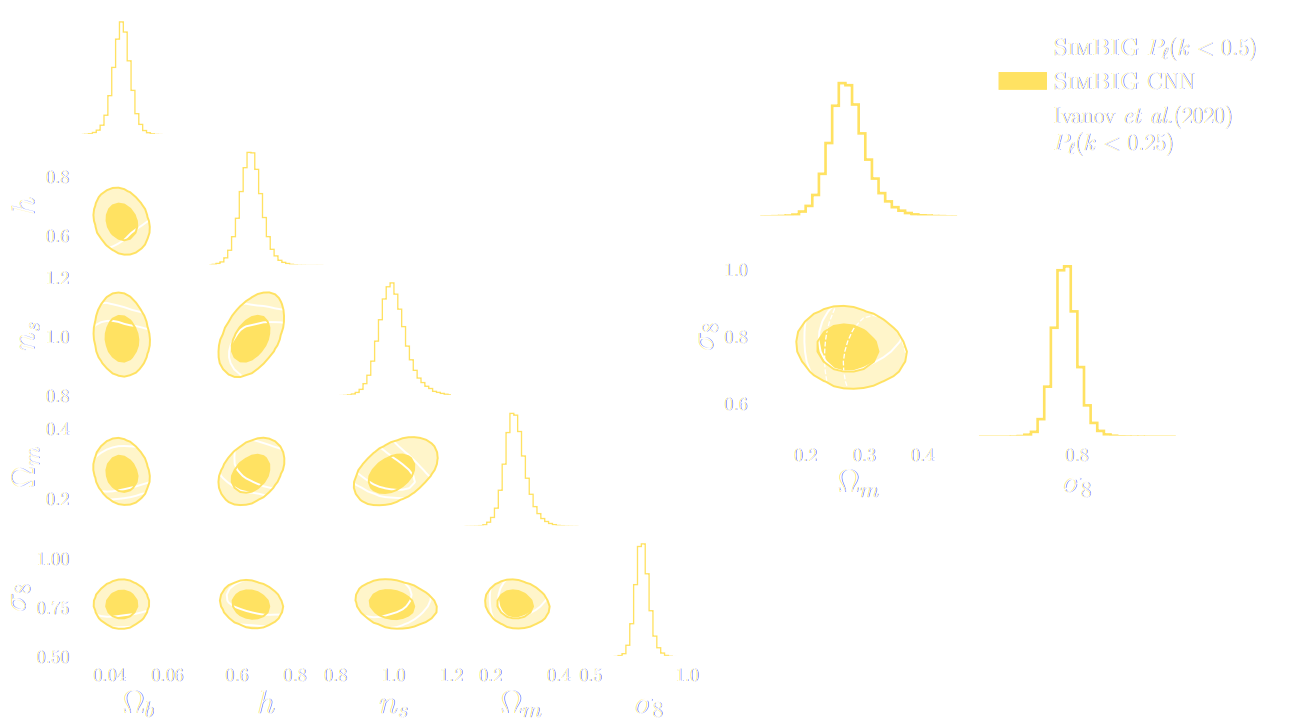
SIMBIG: Field-level SBI of Large Scale Structure (Lemos et al. 2023)
BOSS CMASS galaxy sample: Data vs Simulations
- 20,000 simulated galaxy samples at 2,000 cosmologies
Example of unforeseen impact of shortcuts in simulations
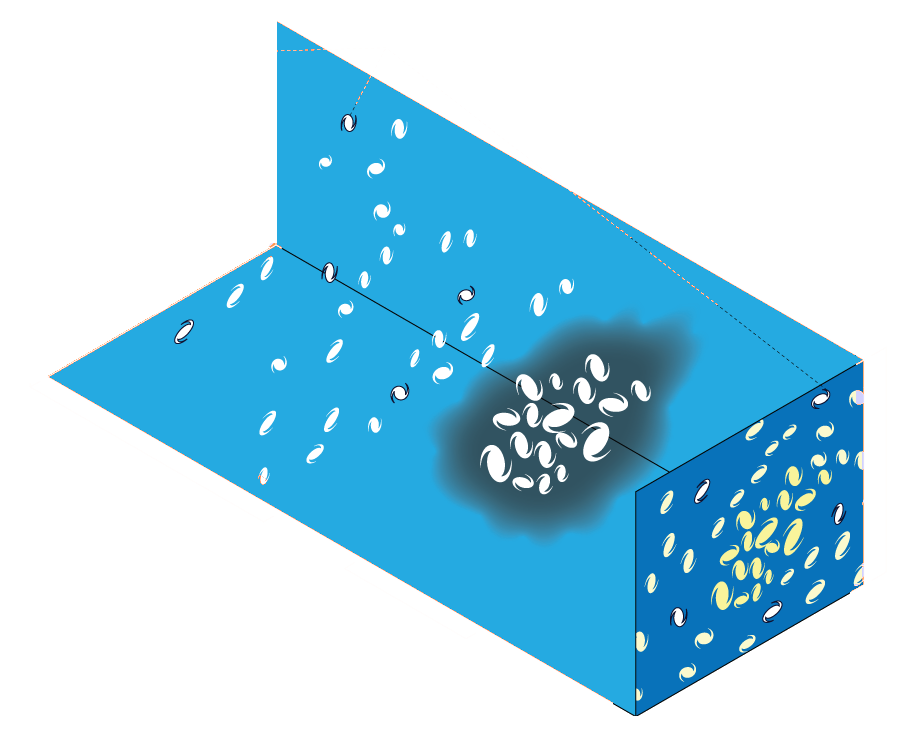
Is it ok to distribute lensing source galaxies randomly in simulations, or should they be clustered?
$\Longrightarrow$ An SBI analysis could be biased by this effect and you would never know it!
How much usable information is there beyond the power spectrum?
$\Longrightarrow$ Can we find non-Gaussian information that is not affected by baryons?
takeways
-
SBI automatizes inference over
numerical simulators.
- Turns both summary extraction and inference problems into an optimization problems
- Deep learning allows us to solve that problem!
-
In the context of upcoming surveys, this techniques provides
many advantages:
- Amortized inference: near instantaneous parameter inference, extremely useful for time-domain.
- Optimal information extraction: no longer need for restrictive modeling assumptions needed to obtain tractable likelihoods.
Will we be able to exploit all of the information content of
LSST, Euclid, DESI?
$\Longrightarrow$ Not rightaway, but it is not the fault of Deep
Learning!
- Deep Learning has redefined the limits of our statistical tools, creating additional demand on the accuracy of simulations far beyond the power spectrum.
- Neural compression methods have the downside of being opaque. It is much harder to detect unknown systematics.
- We will need a significant number of large volume, high resolution simulations.
Explicit Inference
Where the JAX things are
Simulators as Hierarchical Bayesian Models

- If we have access to all latent variables $z$ of the simulator, then the joint log likelihood $p(x | z, \theta)$ is explicit.
- We need to infer the joint posterior $p(\theta, z | x)$ before marginalization to
yield $p(\theta | x) = \int p(\theta, z | x) dz$.
$\Longrightarrow$ Extremely difficult problem as $z$ is typically very high-dimensional. - Necessitates inference strategies with access to gradients of the likelihood. $$\frac{d \log p(x | z, \theta)}{d \theta} \quad ; \quad \frac{d \log p(x | z, \theta)}{d z} $$ For instance: Maximum A Posterior estimation, Hamiltonian Monte-Carlo, Variational Inference.
$\Longrightarrow$ The only hope for explicit cosmological inference is to have fully-differentiable cosmological simulations!
the hammer behind the Deep Learning revolution: Automatic Differentation
- Automatic differentiation allows you to compute analytic derivatives of arbitraty expressions:
If I form the expression $y = a * x + b$, it is separated in fundamental ops: $$ y = u + b \qquad u = a * x $$ then gradients can be obtained by the chain rule: $$\frac{\partial y}{\partial x} = \frac{\partial y}{\partial u} \frac{ \partial u}{\partial x} = 1 \times a = a$$ - This is a fundamental tool in Machine Learning, and autodiff frameworks include TensorFlow and PyTorch.
Enters JAX: NumPy + Autograd + GPU
- JAX follows the NumPy api!
import jax.numpy as np - Arbitrary order derivatives
- Accelerated execution on GPU and TPU

jax-cosmo: Finally a differentiable cosmology library, and it's in JAX!

import jax.numpy as np
import jax_cosmo as jc
# Defining a Cosmology
cosmo = jc.Planck15()
# Define a redshift distribution with smail_nz(a, b, z0)
nz = jc.redshift.smail_nz(1., 2., 1.)
# Build a lensing tracer with a single redshift bin
probe = probes.WeakLensing([nz])
# Compute angular Cls for some ell
ell = np.logspace(0.1,3)
cls = angular_cl(cosmo_jax, ell, [probe])
Current main features
- Weak Lensing and Number counts probes
- Eisenstein & Hu (1998) power spectrum + halofit
- Angular $C_\ell$ under Limber approximation
$\Longrightarrow$ 3x2pt DES Y1 capable
let's compute a Fisher matrix
$$F = - \mathbb{E}_{p(x | \theta)}[ H_\theta(\log p(x| \theta)) ] $$
import jax
import jax.numpy as np
import jax_cosmo as jc
# .... define probes, and load a data vector
def gaussian_likelihood( theta ):
# Build the cosmology for given parameters
cosmo = jc.Planck15(Omega_c=theta[0], sigma8=theta[1])
# Compute mean and covariance
mu, cov = jc.angular_cl.gaussian_cl_covariance_and_mean(cosmo,
ell, probes)
# returns likelihood of data under model
return jc.likelihood.gaussian_likelihood(data, mu, cov)
# Fisher matrix in just one line:
F = - jax.hessian(gaussian_likelihood)(theta)
- No derivatives were harmed by finite differences in the computation of this Fisher!
- Only a small additional compute time compared to one forward evaluation of the model
Inference becomes fast and scalable
- Current cosmological MCMC chains take days, and typically require access to large computer clusters.
- Gradients of the log posterior are required for modern efficient and scalable inference techniques:
- Variational Inference
- Hamiltonian Monte-Carlo
- In jax-cosmo, we can trivially obtain exact gradients:
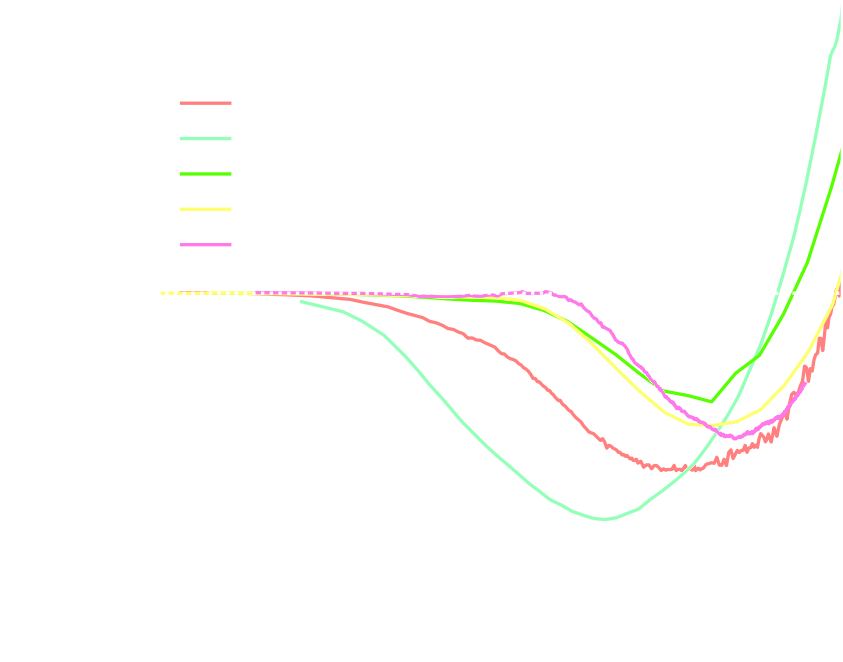
def log_posterior( theta ): return gaussian_likelihood( theta ) + log_prior(theta) score = jax.grad(log_posterior)(theta) - On a DES Y1 analysis, we find convergence in 70,000 samples with vanilla HMC, 140,000 with Metropolis-Hastings
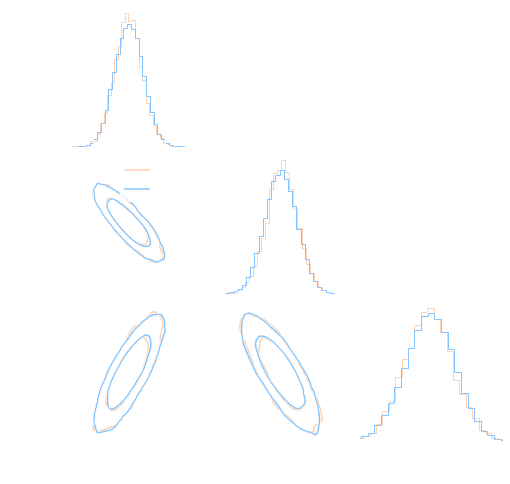
DES Y1 posterior, jax-cosmo HMC vs Cobaya MH
(credit: Joe Zuntz)
Forward Models in Cosmology
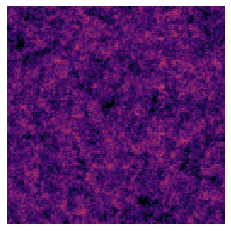 Linear Field
Linear Field
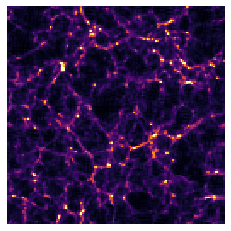 Final Dark Matter
Final Dark Matter
 Dark Matter Halos
Dark Matter Halos
 Galaxies
Galaxies
$\longrightarrow$
N-body simulations
$\longrightarrow$
Group Finding
algorithms
Group Finding
algorithms
$\longrightarrow$
Semi-analytic &
distribution models
Semi-analytic &
distribution models
You can try to learn the simulation...
Learning particle displacement with a UNet. S. He, et al. (2019)

The issue with using deep learning as a black-box
- No guarantees to work outside of training regime.
- No guarantees to capture dependence on cosmology accurately.
the Fast Particle-Mesh scheme for N-body simulations
The idea: approximate gravitational forces by estimating densities on a grid.- The numerical scheme:
- Estimate the density of particles on a mesh
=> compute gravitational forces by FFT - Interpolate forces at particle positions
- Update particle velocity and positions, and iterate
- Estimate the density of particles on a mesh
- Fast and simple, at the cost of approximating short range interactions.


$\Longrightarrow$ Only a series of FFTs and interpolations.
introducing FlowPM: Particle-Mesh Simulations in TensorFlow


import tensorflow as tf
import flowpm
# Defines integration steps
stages = np.linspace(0.1, 1.0, 10, endpoint=True)
initial_conds = flowpm.linear_field(32, # size of the cube
100, # Physical size
ipklin, # Initial powerspectrum
batch_size=16)
# Sample particles and displace them by LPT
state = flowpm.lpt_init(initial_conds, a0=0.1)
# Evolve particles down to z=0
final_state = flowpm.nbody(state, stages, 32)
# Retrieve final density field
final_field = flowpm.cic_paint(tf.zeros_like(initial_conditions),
final_state[0])
- Seamless interfacing with deep learning components
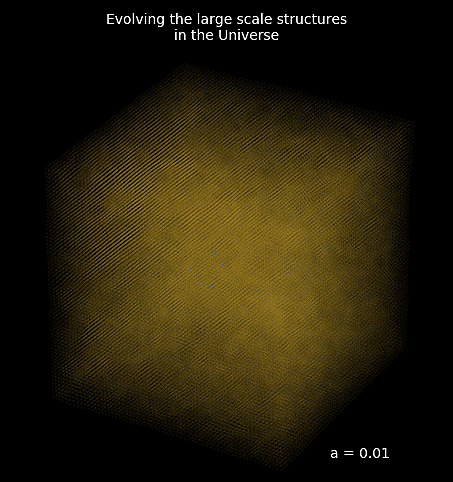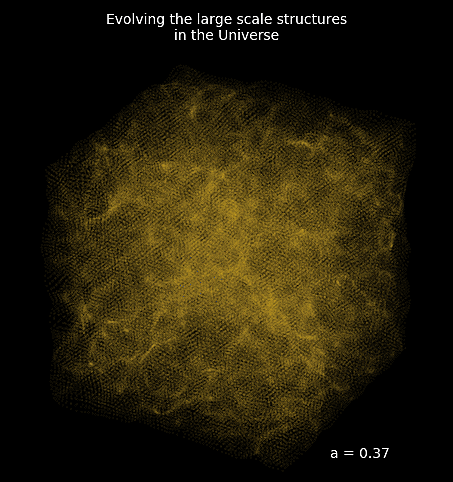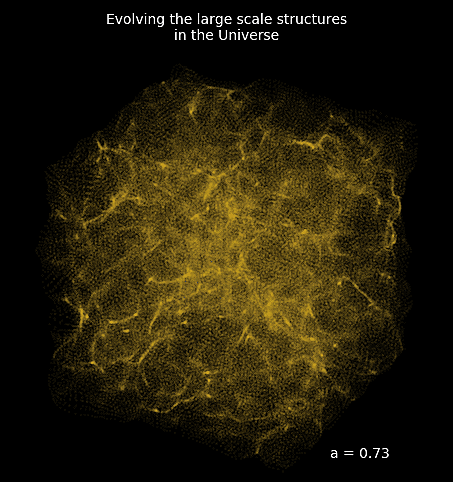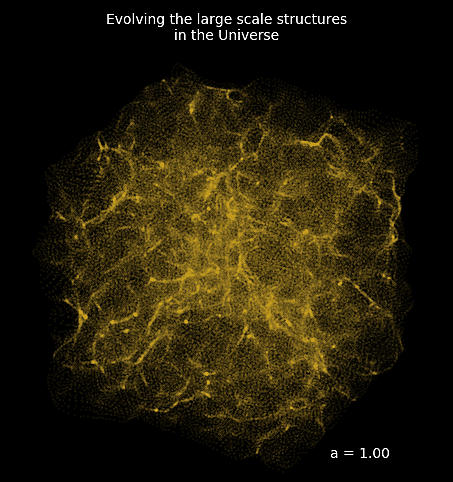
Mesh FlowPM: distributed, GPU-accelerated, and automatically differentiable simulations

- We developed a Mesh TensorFlow implementation that can scale on GPU clusters (horovod+NCCL).
- For a $2048^3$ simulation:
- Distributed on 256 NVIDIA V100 GPUs
- Don't hesitate to reach out if you have a use case for model parallelism!
![]()
- Now developing the next generation of these tools in JAX
Hybrid Physical-Neural ODEs for Fast N-body Simulations


Work led by
Denise Lanzieri
$\Longrightarrow$ Learn residuals to known physical equations to improve accuracy of fast PM simulations.
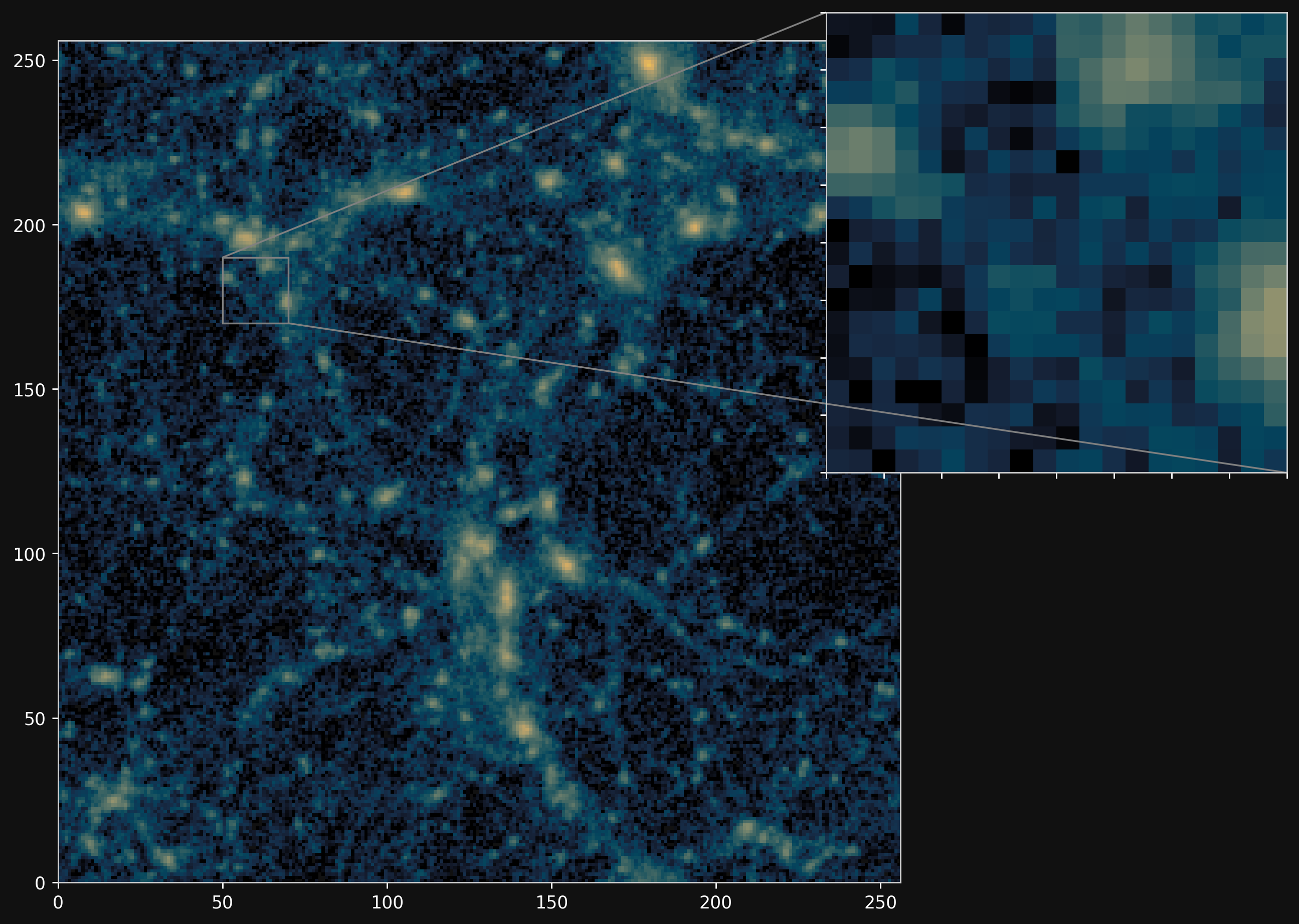
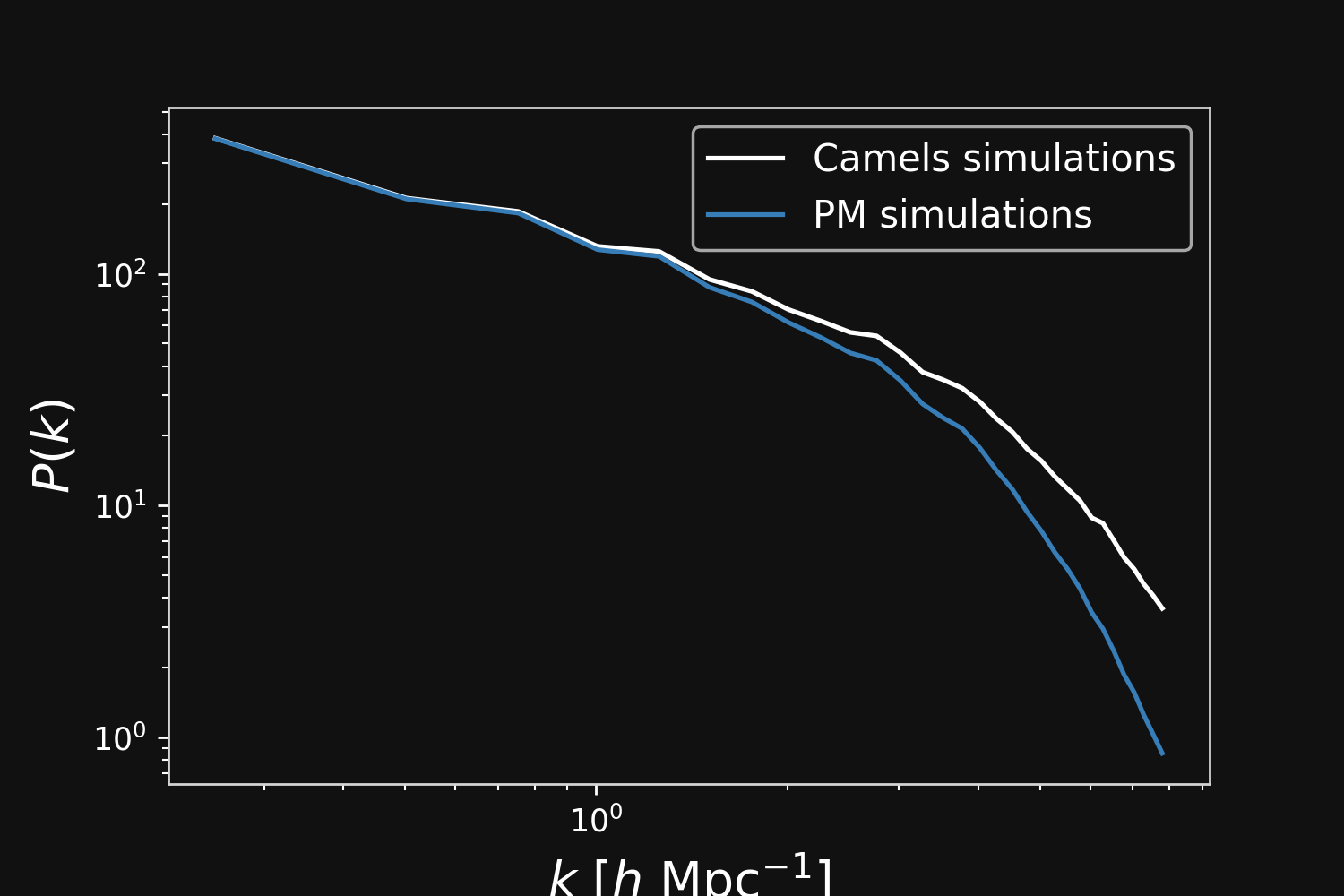
Fill the gap in the accuracy-speed space of PM simulations
Camels simulations
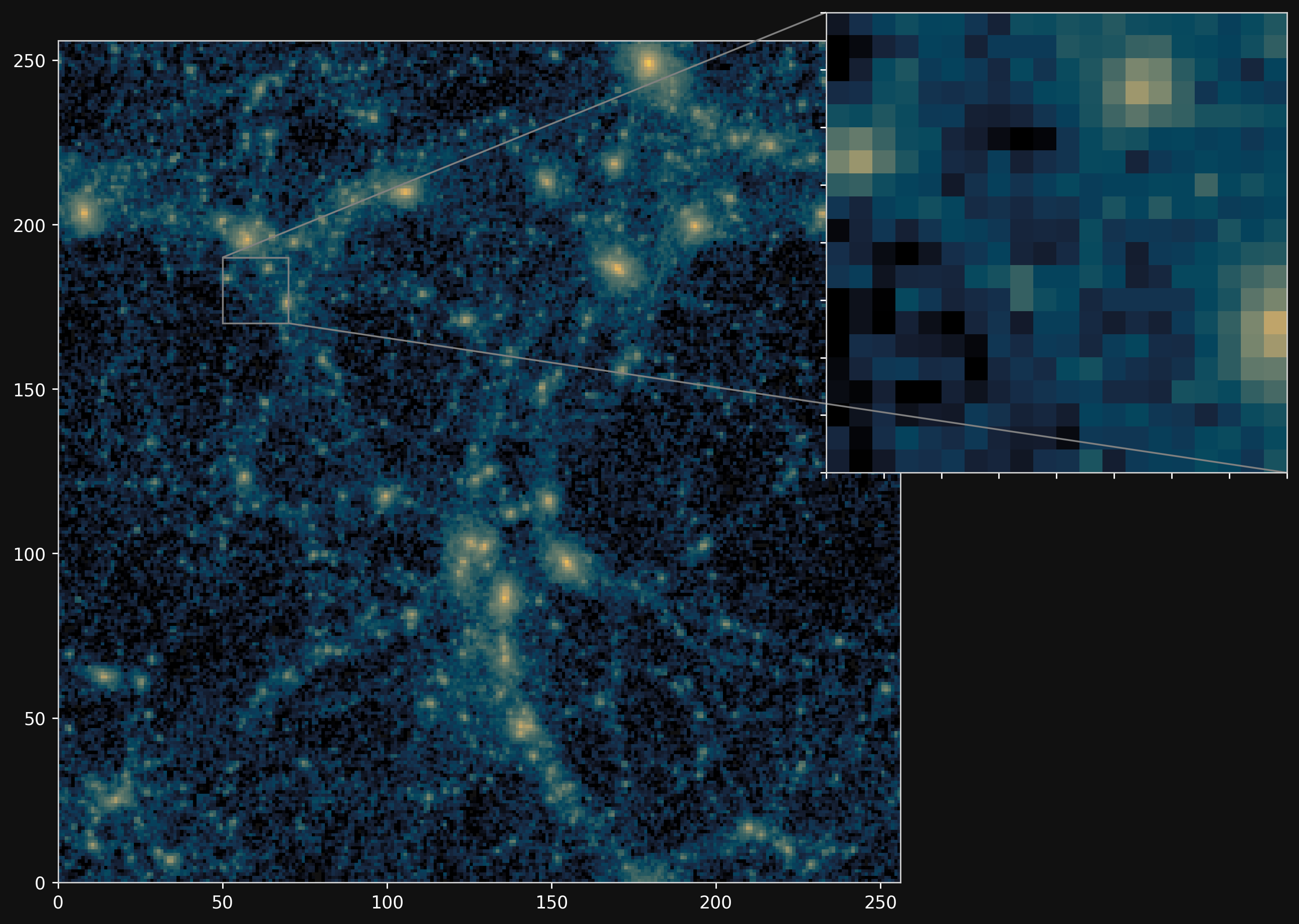
PM simulations
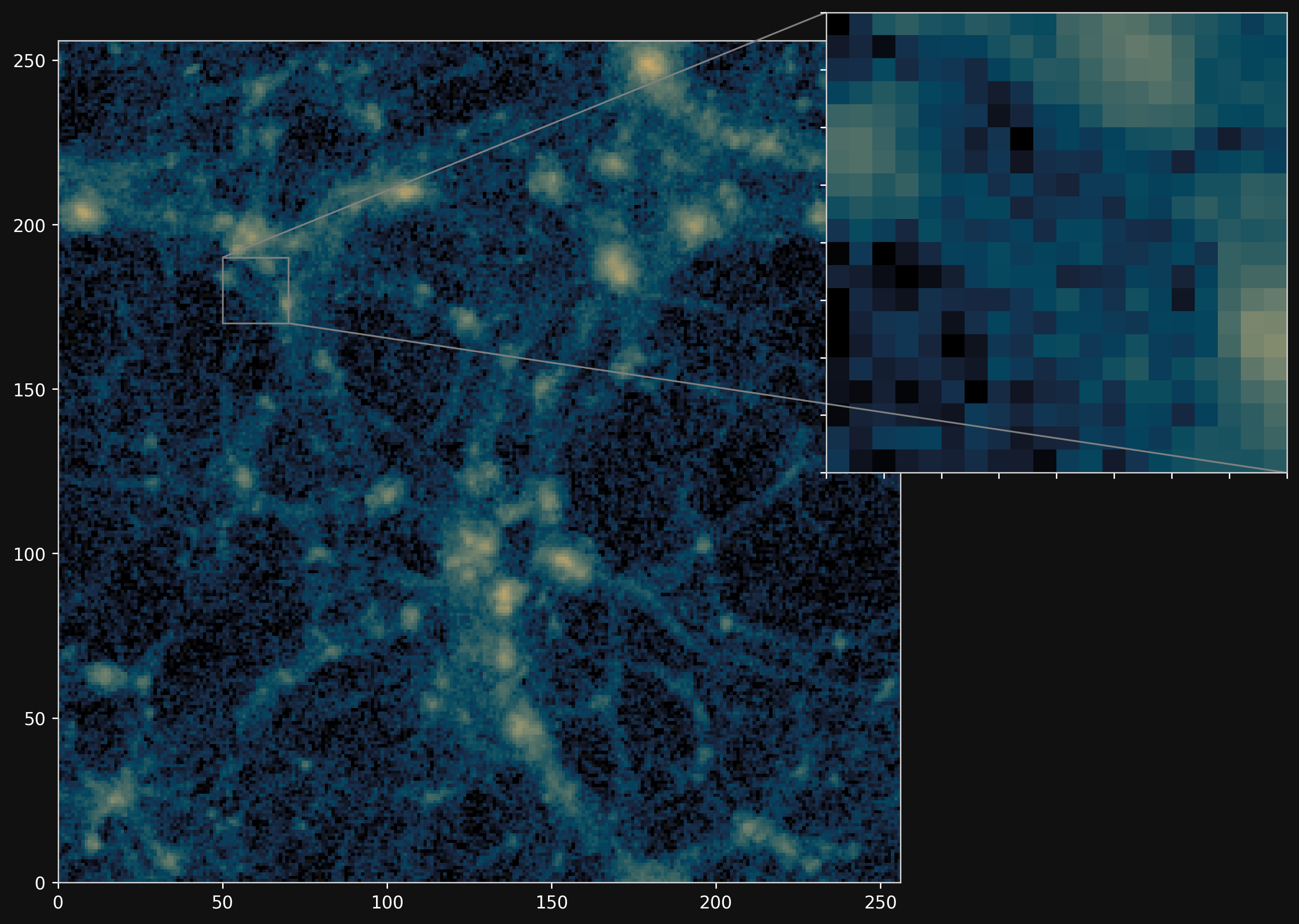
Hybrid physical/neural differential equations
$$\left\{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{d \color{#6699CC}{\mathbf{x}} }{d a} & = \frac{1}{a^3 E(a)} \color{#6699CC}{\mathbf{v}} \\ \frac{d \color{#6699CC}{\mathbf{v}}}{d a} & = \frac{1}{a^2 E(a)} F_\theta( \color{#6699CC}{\mathbf{x}} , a), \\ F_\theta( \color{#6699CC}{\mathbf{x}}, a) &= \frac{3 \Omega_m}{2} \nabla \left[ \color{#669900}{\phi_{PM}} (\color{#6699CC}{\mathbf{x}}) \right] \end{array} \right. $$- $\mathbf{x}$ and $\mathbf{v}$ define the position and the velocity of the particles
- $\phi_{PM}$ is the gravitational potential in the mesh
$\to$ We can use this parametrisation to complement the physical ODE with neural networks.
$$F_\theta(\mathbf{x}, a) = \frac{3 \Omega_m}{2} \nabla \left[ \phi_{PM} (\mathbf{x}) \ast \mathcal{F}^{-1} (1 + \color{#996699}{f_\theta(a,|\mathbf{k}|)}) \right] $$
Correction integrated as a Fourier-based isotropic filter $f_{\theta}$ $\to$ incorporates translation and rotation symmetries
Projections of final density field
Camels simulations
![]()

PM simulations
![]()

PM+NN correction
![]()

Results
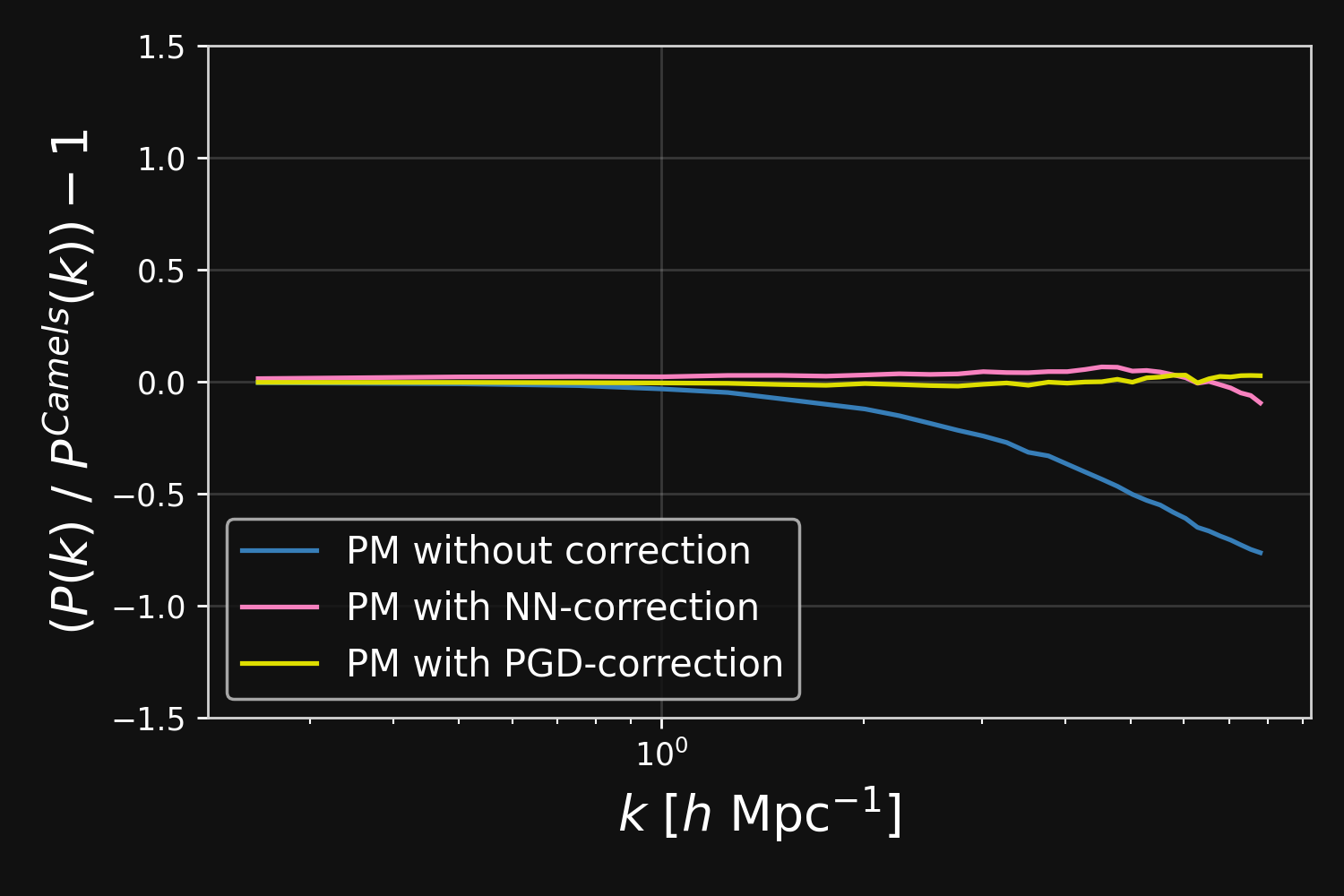
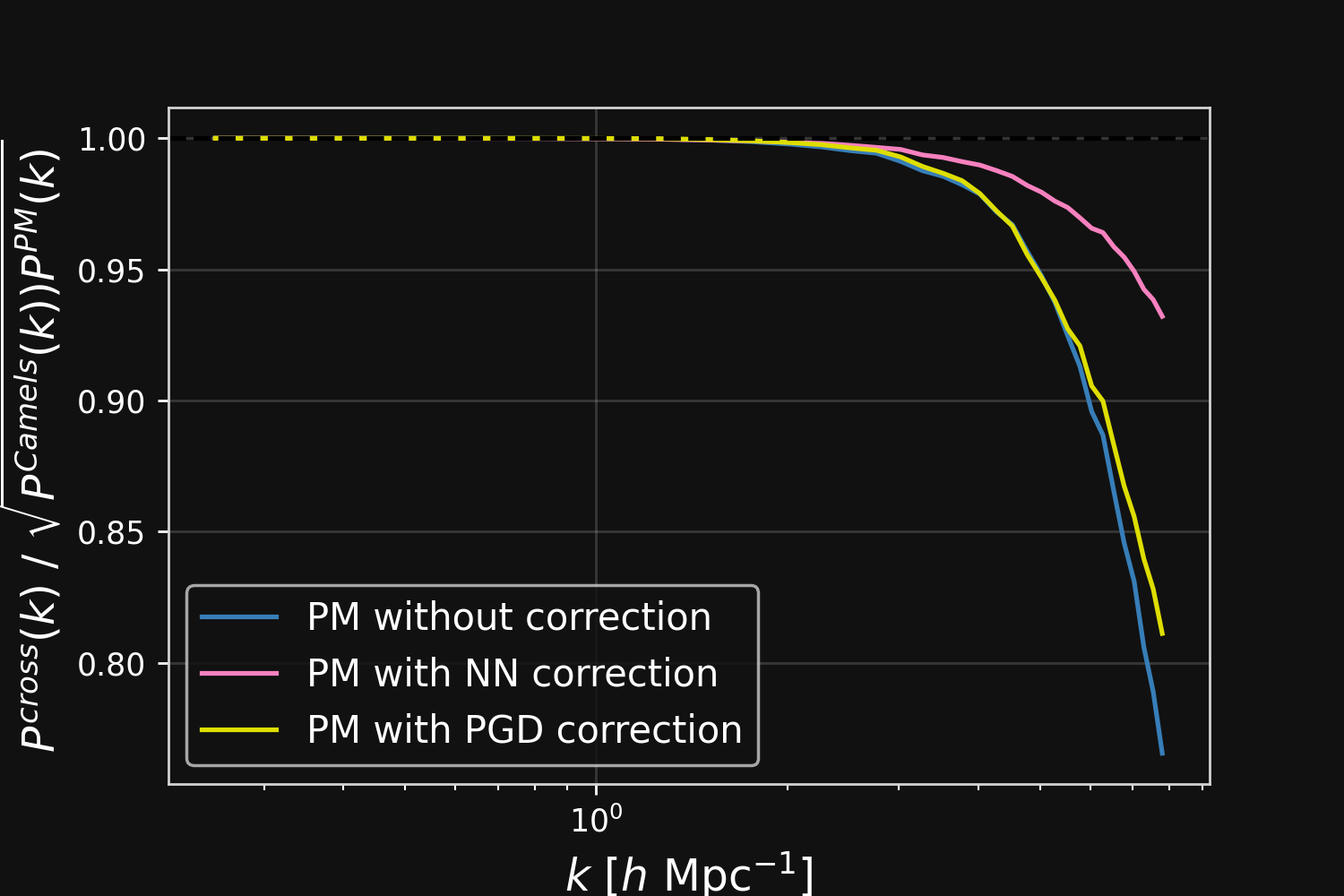
How well does explicit inference work?
Explicit Field level inference for weak lensing (Porqueres et al. 2023)
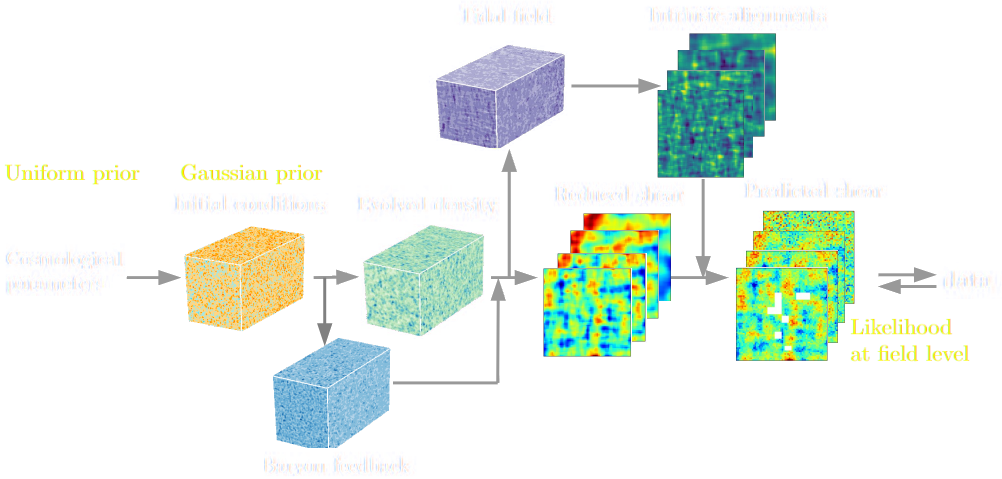
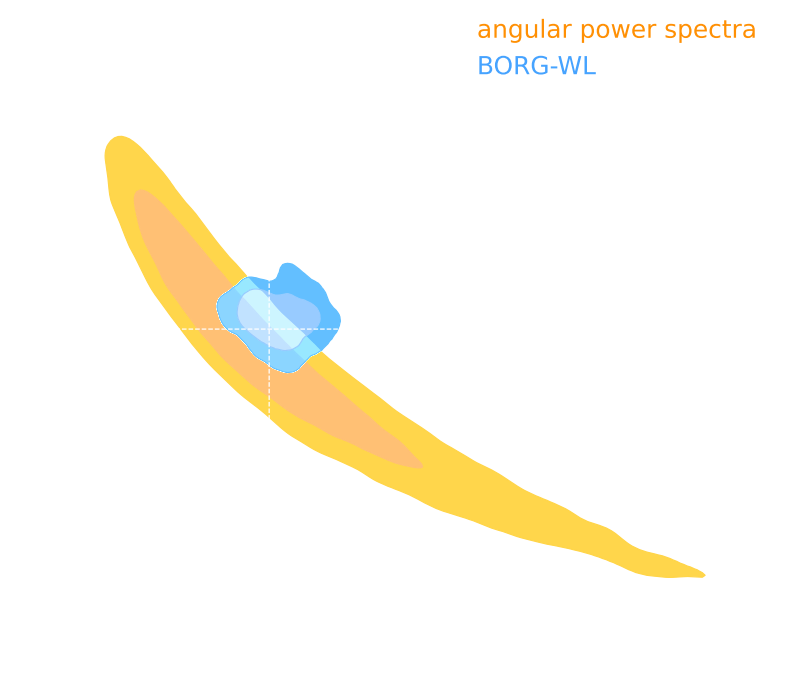
Conclusion
Conclusion
Methodology for inference over simulators
- A change of paradigm from analytic likelihoods to simulators as physical model.
- State of the art Machine Learning models enable Likelihood-Free Inference over black-box simulators.
- Progress in differentiable simulators and inference methodology paves the way to full inference over probabilistic model.
- Ultimately, promises optimal exploitation of survey data, although the "information gap" against analytic likelihoods in realistic settingns remains uncertain.
Thank you!